

< Previous | Contents | Next >
Section 6 Welding Consumables
601. General
1. Application
(1) The covered electrodes for manual welding and gravity welding, wire/flux combinations for two run or multirun submerged arc welding, solid wire/gas combinations for arc welding, flux cored wires with or without gas for arc welding and consumables for use in electroslag and electrogas vertical welding specified in the Rules are to be approved by the Society in accordance with the requirements in this Section.
(2) The welding consumables which are used in welding processes differing from those specified in
(1) or where it is considered impracticable to apply the requirements in this Section are to be of the type approved by the Society.
![]()
![]()
(3) The approval test for welding consumables which are not covered by this Section is to be left to the discretion of the Society. See Guidance
2. Process of manufacture
The approved welding consumables are to be manufactured of uniform quality, under the manu- facturer's responsibility, by the process approved by the Society, at works approved by the Society.
3. Test assemblies
(1) The test assemblies are to be prepared under the supervision of the Surveyor, and all tests are to be carried out in his presence.
(2) When a welded joint is performed, the edges of the plates are to be bevelled either by mechan- ical machining or by oxygen cutting; in the later case, a descaling of the bevelled edges is
necessary.
(3) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler mate-
rial is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
4. Approval test
(1) The approved welding consumables are subject to the approval tests and inspections specified in
602. to 609. in this Section.
(2) Welding consumables are to be approved at each manufacturing plant and for each brand.
However, where are specified in (a) and/or (b) below, a reduced test programme at least equiv- alent to annual tests is permitted if the manufacturer can certify that the materials used and the
fabrication process are identical with those used in the main works. However, should there be
any doubt, complete test-series may be required.
(a) Where welding consumables which have been approved are intended to manufacture at man-
ufacturing plants other than those of the manufacturers who manufacture the said welding consumables.
(b) Where welding consumables which have been approved are intended to manufacture accord-
ing to technical licensing agreements with those parties who manufacture the said welding consumables.
(3) Wire flux combination for submerged arc welding. If a unique powder flux is combined with
different wires coming from several factories belonging to the same firm, it may be admitted to perform only one test-series if the different wires are conformable to the same technical specifi- cation, after approval of the Society.
(4) Where deemed necessary by the Society, tests other than those specified in this Section may be required.
5. Periodical inspection
The manufacturer of welding materials is to be subjected to the periodical inspection in the pres- ence of Surveyor for each brands of the welding materials at each manufacturing plant in a period not exceeding 12 months.
6. Alterations to approved consumables
(1) In case when the particulars of the welding materials which being mentioned in the certificate
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 145
![]()
of approval, such gas, are changed,
as grade, welding position, maximum diameter of welding materials or shield the manufacturer is to submit a copy of application form for change to the
Society, and necessary additional approval tests are to be carried out accordingly.
(2) When the significant changes in compositions or manufacturing process of the wire and flux or removal of manufacturing plant is made, the manufacturer is to submit a single copy of notifi-
cation of alternation in any preferred form to the Society, and necessary confirmation survey and test may be carried out accordingly.
(3) Upgrading and uprating of welding consumables will be considered only at manufacturer's re- quest, preferably at the time of annual testing. Generally, for this purpose, tests from butt weld assemblies will be required in addition to the normal annual approval tests.
7. Retests
(1) Tensile test and bend test
(a) Where the tensile test and bend test fail to meet the requirements, twice as many test speci- mens as the number of specimens of failed test are to be selected from the first test materi- al or from a test material welded under the same welding conditions, and if all of test specimens pass the tests, then the tests are considered to be successful.
(b) Where insufficient original welded assembly is available, a new assembly is to be prepared using welding consumables from the same batch.
(c)
If the new assembly is made with the same procedure (particularly the number of runs) as
the original assembly, only the duplicate re-test specimens needs to be prepared and tested. Otherwise, all test specimens should be prepared as for re-testing.
(2) Impact test
(a) Where the result of the impact test is unsatisfactory, additional tests may be carried out, with the exception of the cases specified in (i) and (ii) below, by taking a set of test speci-
mens out of the same test material from which the above-mentioned test specimens have been taken.
(i) The absorbed energy of all test specimens is under the required average absorbed energy.
(ii) The absorbed energy of two of the test specimens is under 70 % the required average absorbed energy.
(b) In case of the previous (a), the test specimens may be accepted, provided that the average
absorbed energy of the six test specimens, including those which have been rejected as un- satisfactory, is not less than the required average absorbed energy, and that not more than two individual results are lower than the required average absorb energy and of these, not
more than one result is below 70 % of the required average absorbed energy.
(3) Where the retest fails to meet the requirements, the test may be made over again with changed welding conditions. In this case, if the whole tests specified for the test assembly are carried
out and are in compliance with the requirements, the test is accepted as successful.
8. Revocation of approval
In the following cases, the approval of welding consumables by the Society shall be revoked, after notice is given to the manufacturer:
(1) When the Society has recognized that the quality is remarkably worse than that approved or is not uniform.
(2) When the welding consumables have failed the requirements in the annual inspections.
(3) When the welding consumables are not inspected annually as required by the Rules.
9. Data
The Society may require the submission of the data with respect to the properties of welding con- sumables if necessary.
10. Packings and markings
(1) The approved welding consumables are to be packed throughly to keep the quality during their transportation and storage.
(2) All packages of approved welding consumables are to clearly marked with the following de- scriptions together with the approved mark of the Society.
(a)
(b)
Brand
Name of manufacturer
![]()
146 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(g)
(h)
(i)
Kind of gas if used
Grade or mark of welding consumables Electric current and its polarity Welding positions
Date and number of production
Sizes (diameter of core wire, length of elect rode, grain size of flux for submerged arc
welding, etc.)
Special notices on the treatment
602. Electrodes for manual arc welding for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low temperature service
1. Application
(1) Electrodes for manual arc welding for normal strength steels, higther strength steels and steels for low temperature service given in the following (a) and (b) (hereinafter referred to as "electrodes") are to be subjected to the approval test and annual inspections in accordance with the requirements in 602.
(a) Electrodes for manual welding
(i) For butt welds
(ii) For fillet welds
(iii) For both butt welds and fillet welds
(b) Electrodes used in gravity welding or similar set-ups
(i) For fillet welds
(ii) For both butt welds and fillet welds
![]()
(2) Any requirements regarding one side welding without backing are left to the discretion of the Society. See Guidance![]()
2. Grades and marks of electrode
(1) Electrodes are classified as specified in Table 2.2.16.
Table 2.2.16 Grades and Marks
For normal strength steel | For higher strength steel | For steel for low temperature service |
1, 2, 3 | 2Y, 3Y , 4Y , 5Y , 2Y40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 | L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 |
(2) For low hydrogen electrodes which have passed the hydrogen test specified in Par 6, the suf- fixes given in Table 2.2.22 are to be added to the grade marks of the said electrodes. (e.g. 2Y H 5)
3. General provisions for tests
![]()
![]()
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimension of test assemblies, diameter of electrodes used for welding, welding positions, grades and number of test specimens to be taken from each test assembly for electrodes given in Par 1 (1) (a) (i) and (iii) are to be as given in Table 2.2.17. However, where deemed necessary by the Society, hot cracking tests may be required by the Society in addition to tests specified in this Table. See Guidance
(2) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimension of test assemblies, diameter of electrodes used
for welding and welding positions, together taken from each test assembly for electrodes
Table 2.2.18.
(3) Tests for electrodes given in Par 1 (1) (b) the following (a) and (b):
with grades and number of test specimens to be given in Par 1 (1) (a) (ii), are to be as given in
are to be in accordance with the requirements in
(a) For electrodes given in Par 1 (1) (b) (i), tests given in Table 2.2.18 specified in the pre- ceding (2) are to be conducted.
(b) For electrodes given in Par 1 (1) (b) (ii), tests specified in the preceding (a) and butt weld test given in Table 2.2.17 specified in the preceding (1) are to be conducted.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 147
![]()
Table 2.2.17 Kinds of Test for Electrode
Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and No. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||||
Welding position | Diameter of electrode (mm) | No. of test assemblies | Dimensions of test assembly | Thickness (mm) | ||
Deposited metal test | Flat | 4 | 1(1) | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3 |
max. diameter | 1(1) | |||||
Butt weld test | Flat | First run. 4; Subsequent runs:5 or over; Last two runs. max. dia. | 1 | Fig 2.2.20 | 15~20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Face bend specimen : 1 Root bend specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3(5) |
First run. 4; Second run,5 or 6; Subsequent runs. max. dia. | 1(2) | |||||
Horizontal (4) | First run. 4 or 5 Subsequent runs, 5 | 1 | ||||
Vertical upward | First run. 3.2; Subsequent runs. 4 or 5 | 1 | ||||
Vertical downward | (3) | 1 | ||||
Overhead | First run. 3.2; Subsequent runs. 4 or 5 | 1 | ||||
Fillet weld test(6) | Horizontal | One side; max. dia. The other side; min. dia. | 1 | Fig 2.2.21 | 20 | Macro structure test specimen : 3(8) Hardness test specimen : 3 (8) Fracture test specimen : 2 |
Hydrogen test(7) | Flat | 4 | 4 | (9) | 12 | Hydrogen test specimen : 1 |
NOTES: (1) Where the diameter of the manufactured electrodes is of one type, there is to be one test assembly. (2) Where the tests are conducted solely in the downhand position, this test assembly has been added. (3) Electrodes with diameters specified by the manufacturers are to be used. (4) For electrodes which have passed butt weld tests in the downhand and vertical upward positions, test in the horizontal position may be omitted subject to approval by the Society. (5) Impact tests are not to conduct for overhead welds. (6) This test is added solely for electrodes used in both butt welds and fillet welds. (7) This test is to conduct solely for low hydrogen electrodes. (8) Test specimens used in macro structure test and hardness tests are considered to be the same. (9) Dimensions of test assembly are to be as specified in 602. 6. | ||||||
(4) Where electrodes are intended to be used for both items specified in Par 1 (1) (a) and (b), ap- proval tests required for each electrode are to be conducted. However, deposited metal tests may be omitted for electrodes given in Par 1 (1) (b).
(5) Steel plates to be used in preparation of test assemblies are to be as given in Table
cording to the grades of electrode.
2.2.19 ac-
(6) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met- al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
(7) For the approval of electrodes, the tests
ducted for each brand of electrodes.
(8) After welding, the test assemblies are not
specified in the preceding (1) to (4) are to be con-
to be subjected to any heat treatment.
![]()
148 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.18 Kinds of Test for Electrode
Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and No. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||||
Welding position | Diameter of electrode (mm) | No. of test assemblies | Dimensions of test assembly | Thickness (mm) | ||
Deposited metal test | Flat | 4 | 1 | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3 |
max. diameter | 1 | |||||
Fillet weld test | Flat | One side; max. dia. The other side; min. dia. | 1 | Fig 2.2.20 | 20 | Macro structure test specimen : 3(1) Hardness test specimen : 3(1) Fracture test specimen : 2 |
Horizontal- vertical | 1 | |||||
Vertical upward | 1 | |||||
Vertical downward | 1 | |||||
Overhead | 1 | |||||
Hydrogen test(2) | Flat | 4 | 4 | (3) | 12 | Hydrogen test specimen : 1 |
NOTES: (1) Test specimens used in macro tests and hardness tests are considered to be the same. (2) This test is to conduct solely for low hydrogen electrodes. (3) Dimensions of test assembly are to be as specified in 602. 2. 6. | ||||||
Table 2.2.19 Grade of Steels used for Test Assembly
Grade of electrode | Grade of steels used for test assembly(1)(2) |
1 | A |
2 | A , B or D |
3 | A , B , D or E |
2Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32 or D H 36 |
3Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32 or E H 36 |
4Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
5Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
2Y 40 | A H 40 or D H 40 |
3Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40 or E H 40 |
4Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
5Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
L 1 | E o r R L 24A |
L 2 | E , R L 235A , R L 235B , R L 325A or R L 325B |
L 3 | R L 325A , R L 325B or R L 360 |
L 91 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
L 92 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
NOTES: (1) Notwithstanding the requirements in this Table normal strength or higher strength steel may be used for the deposited metal test assembly. In this case, test assemblies of grade L 91 and L 92 are to be appro- priately buttered. (2) The tensile strength of higher strength steels A H 32, D H 32 E H 32, and F H 32 used in butt weld test as- semblies is to be greater than 490 . | |
![]()
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 149
![]()
(9) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as- certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
4. Deposited metal test
(1) Welding of deposited metal test assemblies
(a) Test assembly as shown in Fig 2.2.18 is to be welded in the downhand position according to the normal practice.
(b)
The weld metal is to be deposited in single or multi-run layers according to normal prac- tice, and the direction of each run is to alternate from each end of the plate, each run of
weld metal being not less than 2 mm but not more than 4 mm thick.
![]()
![]()
(c) After each run, the test assembly is to be left in still air until it has
cooled to less than
250 but not below 100 , the temperature being taken at the surface of seam.
centre
of the weld on the
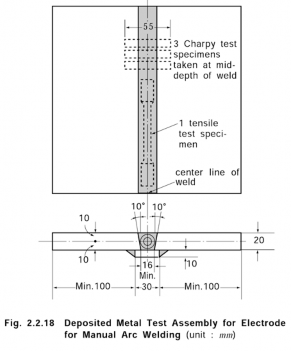
(2) Chemical analysis
The chemical analysis of the deposited weld metal in each test assembly is to be supplied by the manufacturer and is to include the content of all significant alloying element.
(3) Deposited metal tensile test
![]()
(a) The tensile test specimen, one from each test assembly, is to be machined to dimensions R14A test specimen as shown in Table 2.2.1, care being taken that the longitudinal axis coincides with the centre of weld and the mid-thickness of plates.
(b)
(c)
The tensile test specimen may be subjected to a temperature not exceeding 250 for a pe- riod not exceeding 16 hours for hydrogen removal prior to testing.
The tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of each test specimen are to comply with
the requirements given in Table 2.2.20, where the upper limit of tensile strength is ex- ceeded, special consideration will be given to the approval of the electrode, taking into con-
sideration of the other mechanical properties shown in the test results and the chemical composition of deposited metal.
(4) Deposited metal impact tests
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di- mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimen as shown in Table 2.1.3. The test speci-
men is to be cut with its longitudinal axis transverse to the direction of welding, and the test specimen is to coincide with the mid-thickness of the plate shown in Fig 2.2.19.
(b) The notch is to be positioned in the specimens perpendicular to the surface
centre of weld and is to be cut in the face of test of plate.
![]()
150 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()

Fig 2.2.19 Position of Butt Weld Impact Test Specimen (Unit : mm, t : plate thickness)
(c) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the
Table 2.2.20.
requirements given in
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.20 Tensile and impact Test Requirements for Deposited Metal
Grade of electrode | Tensile strength ( ) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation ( ) | Impact test | |
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy(J) | ||||
1 | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | 20 | 47 min. |
2 | 0 | ||||
3 | -20 | ||||
2Y | 490 660 | 375 min. | 22 min. | 0 | |
3Y | -20 | ||||
4Y | -40 | ||||
5Y | -60 | ||||
2Y 40 | 510 690 | 400 min. | 22 min. | 0 | |
3Y 40 | -20 | ||||
4Y 40 | -40 | ||||
5Y 40 | -60 | ||||
L 1 | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | -40 | 34 min. |
L 2 | 440 610 | 345 min. | 22 min. | -60 | |
L 3 | 490 660 | 375 min. | 21 min. | -60 | |
L 91 | 590 min. | 375 min.(1) | 25 min. | -196 | 27 min. |
L 92 | 660 min. | 410 min.(1) | 25 min. | -196 | |
NOTE: (1) 0.2 % Yield strength | |||||
![]()
![]()
(d) When the absorbed energy of two or more test specimens among a set of test specimens is less in value than the specified average absorbed energy or when the absorbed energy of a single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the specified average absorbed energy, the test is considered to have failed.
5. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies
![]()
(a) Test assembly as shown in Fig 2.2.20 is to be welded in each welding position (flat, hori- zontal-vertical, vertical-upward, vertical downward and overhead) which is recommended by the manufacturer, according to the normal practice.
![]()
(b) Test assembly is to be left in still air until it has cooled to less than 250 but not below
100 , the temperature being taken at the centre of the weld on the surface of seam.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 151
![]()
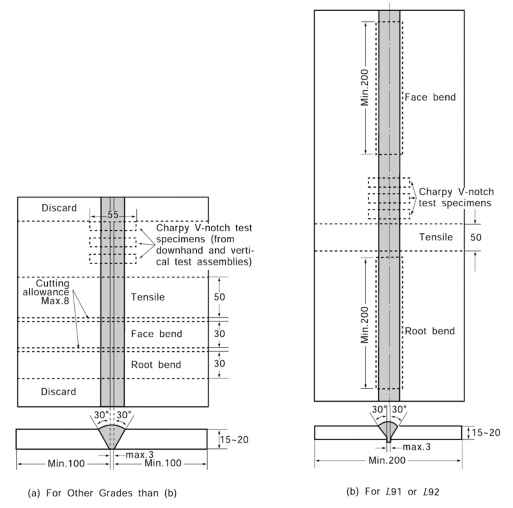
Fig 2.2.20 Butt weld Test Assembly for Electrode for Manual Arc Welding (Unit: mm)
(c) In all cases, the back sealing runs are to be made with 4 mm electrode in the welding po- sition appropriate to each test assembly, after cutting out the root run to clean metal. For electrodes suitable for downhand welding only, the test assemblies may be turned over to carry out the back sealing run.
(2) Butt weld tensile tests
(a) The tensile test specimen is to be R 2A specimen shown in Table 2.2.1 and the test speci- men is to be taken from each test assembly.
(b)
(c)
The surface of weld is to be machined flush with the surface of plate.
The tensile strength of test specimen is to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.21.
(3) Butt weld bend test
(a) The face and root bend test specimens are to be R B 4 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2, and test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly. However, for L 91 or L 92, the
face and root bend specimens are to be R B 1 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2, and test
specimens are to be taken longitudinally from each test assembly.
(b)
(c)
The upper and lower surfaces of the weld are to be filed, ground or machined flush with the Surface of the plate and the sharp corners of the specimens rounded to a radius not ex- ceeding 2 mm.
The test specimens are to be capable of withstanding, without crack exceeding 3 mm long on the outer surface of other defects, being bent through an angle of 120 degrees over a
former having a radius of 1.5 times the thickness of test specimen. The radius and angle of the former for L 91 and L 92, however, are to be 2 times the thickness of the specimen and 180degrees respectively.
![]()
152 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.21 Tensile and impact Test Requirements for butt weld
Grade of electrode | Tensile strength ( ) | Impact test | ||
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | |||
Flat, Horizontal, Overhead | Vertical upward Vertical downward | |||
1 | 400 min. | 20 | 47 min. | 34 min. |
2 | 0 | |||
3 | -20 | |||
2Y | 490 min. | 0 | ||
3Y | -20 | |||
4Y | -40 | |||
5Y | -60 | |||
2Y 40 | 510 min. | 0 | 39 min. | |
3Y 40 | -20 | |||
4Y 40 | -40 | |||
5Y 40 | -60 | |||
L 1 | 400 min. | -40 | 27 min. | 27 min. |
L 2 | 440 min. | -60 | ||
L 3 | 490 min. | -60 | ||
L 91 | 630 min. | -196 | ||
L 92 | 670 min. | -196 | ||
(4) Butt weld impact tests
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di- mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimens as shown in Table 2.1.3.
(b)
(c)
(d)
The test specimens are to be prepared as shown in Fig 2.2.19 and the dimensions, form, position and direction of notches are to be as specified in Par 4. (4)
Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.21, appropriate to the grades of the electrode and welding position.
When the absorbed energy of two or more test specimens among a set of test specimens is
less in value than the specified average absorbed energy or when the absorbed energy of a single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the specified average absorbed energy,
the test is considered to have failed.
6. Hydrogen test
The hydrogen test to be carried out by the mercury method or gas chromatographic method. The use of the glycerine method may be admitted at the Society discretion.
(1) The mercury method to be as specified in the Standard K S B ISO 3690
(2) The gas chromatographic method to be as specified in the Standard KS D0064(Method of Measurement for Hydrogen Evolved from Steel Welds)
(3) Glycerin method
(a) Welding of test assemblies
(i) As a rule, mild and high tensile steels are to be used for the test assembly, and four test specimens are to be prepared measuring 12 mm by 25 mm in cross section by about 125 mm in length. Before welding, the specimens are to be weighed to the nearest 0.1
gram. On the 25 mm surface of each test specimen, a single bead of welding is to be
deposited,
about 100 mm in length, by a 4 mm electrode, using about 150 mm of the
electrode.
current of
![]()
The welding is to be carried out with as short
about 150 .
an arc as possible and with a
(ii) The electrodes, prior to welding, can be submitted to the
mended by the manufacturer.
normal drying process recom-
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 153
![]()
![]()
![]()
(b) Abefteqruewneclhdeidngi,neawcahtertesatt sapetecimmpeenratpurreepaorfedaptoprothxeimhaytedlryog2e0n tesftorsp3e0cifsieecd, ainfte(ra)reamboviengis thtoe slag within a period of 30 sec. Subsequently, the test specimens are to be cleaned and be sealed into a hydrogen collector by means of the glycerin replacement method.
![]()
The glycerin is to be kept at a temperature of approximately 45 during the test. The test time required for all the four test specimens from welding to the enclosure in the hydrogen collector is to be within 30 min. After immersing into glycerin for 48 hours, the test specimens are to be cleaned with water and alcohol and weighed with an accuracy of 0.1 g after being dried to measure the weight of the deposited metal. The volume of hydrogen
![]()
gas collected is to be measured with an accuracy of 0.05 and converted into that under
the conditions 20 and 1 atmospheric pressure (760 mm ).
(4) Average diffusible hydrogen contents of the four specimens is to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.22 according to the test procedures specified in preceding articles or the type of suffixes to be added to the grade marks.
![]()
Table 2.2.22 Requirements for Hydrogen Contents ( )
Mark | Mercury method | gas chromatographic method | Glycerine method |
H 15 | 15 max. | 15 max. | 10 max. |
H 10 | 10 max. | 10 max. | 5 max. |
H 5 | 5 max. | 5 max. | - |
7. Fillet weld test
(1) Welding of fillet weld test assemblies
(a) Test assembly as shown in Fig 2.2.21 is to be welded in each welding position (flat, hori- zon- vertical, vertical-up ward, vertical-downward and overhead) which is recommended by the manufacturer.
(b)
(c)
(d)
The first side is to be welded using the maximum size of electrode manufactured and the second side is to be welded using the minimum size of electrode manufactured.
The leg length of fillet welds may will in general be determined by the electrode size and the welding current employed during testing.
In case of fillet welds using gravity or similar contact welding method, the fillet welding is
to be carried out with electrodes of maximum length. Where approval is requested for the welding of both normal strength and higher strength steel, the assemblies are to be prepared using higher strength steel.
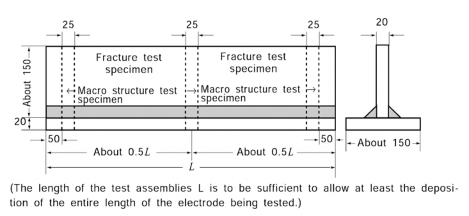
Fig 2.2.21 Fillet Weld Test Assembly (Unit : mm)
(2) Fillet weld macro-structure test
(a) For macro-structure test specimens, those with breadths of 25 mm are selected from three places shown in Fig 2.2.21.
![]()
154 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(b) The macro-etching test is conducted on the transverse section of fillet weld joint and welded
joints are to be free from excessive cracks and other injurious defects.
(3) Fillet weld hardness test The hardness of
difference of leg length between upper and lower,
weld metal, heat affected zone and base metal are to
![]()
![]()
be measured at places given in Fig 2.2.22 for each test specimen which underwent the mac- ro-etching test specified in preceding (1) and the respective hardnesses are to be in accordance with those deemed appropriate by the Society. See Guidance

Fig 2.2.22 Hardness Test (Unit : mm)
(4) Fillet weld fracture test
(a) One of the remaining sections of the fillet weld is to have the weld on the first side goug-
ed or machined to facilitate breaking the fillet weld as shown in Fig 2.2.23, on the second side by closing the two plates together, submitting the root of the weld to tension. On the other remaining section the weld on the second side is to be gouged or machined and the
section fractured using the same procedure.
(b) The fractured surfaces
penetration, or internal
are to be examined and there should be no evidence of incomplete

cracking and they should be reasonably free from porosity.
Fig 2.2.23 Fracture Test
8. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspections, tests specified in the following (2) and (3) are to be conducted for each brand of the approved electrodes and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspections for manual arc welding electrodes are to be as given in Table 2.2.23.
(3) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspections of electrodes used in gravity welding or other welding using similar welding devices are to be as given in Table 2.2.24.
(4) The welding procedures and requirements for test assemblies of tests specified in the preceding
(2) and (3) are to be as specified in Par 4.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 155
![]()
Table 2.2.23 Kind of Test for Annual Inspection
Kind of test(2) | Test assembly | Kind and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||||
Welding position | Diameter of electrode (mm) | Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm) | ||
Deposited metal test | Flat | 4(1) | 1 | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3 |
exceeding 4, 8 max. | 1 | |||||
NOTES: (1) Where deemed necessary by the Society, butt weld tests in the downhand or vertical (either upward or downward) welding position specified in Table 2.2.17 may be requested in place of deposited metal tests of 4 mm diameter electrodes. In this case, impact test specimens (one set of three) are to be selected. (2) For low hydrogen electrodes, an hydrogen test can also be required at the discretion of the Society. | ||||||
Table 2.2.24 Kind of Test for Annual Inspection
Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||||
Welding position | Diameter of electrode (mm) | Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm) | |||
Deposited metal test | Flat | 4 min. | 1 | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3 | |
9. Changes in grades
(1) Where changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness of electrodes approved are to be made, tests specified in the following (2) and (3) are to be carried out and satisfactorily passed in accordance with the requirements in 601. 6 (3).
(2) For changes in the grades relating to strength, the butt weld tests, specified in the annual in- spection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
(3) For changes in the grades relating to toughness, the butt weld impact tests, specified in the an- nual inspection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
603. Automatic welding consumables for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low temperature service
1. Application
(1) Welding consumables for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low tem- perature service given in the following (a) through (c) (hereinafter referred to as "automatic welding consumables") are to be subjected to the approval tests and annual inspections in ac- cordance with the requirements in 603.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Submerged arc automatic welding consumables (Wire flux combinations)
Gas shielded arc automatic welding consumables(Flux cored wire and solid wire automatic welding consumables with shielding gas)
Self-shielded arc automatic welding consumables (flux-cored or flux-coated wires without a shielding gas)
(2) Wire-flux combinations for multiple electrode submerged arc welding will be subject to separate
approval tests. They are to be carried out generally in accordance with the requirements in 603.
(3) At the discretion of the Society, wires or wire-gas combinations approved for semi-automatic multirun welding may also be approved, without additional tests, for automatic multirun welding approval. This is generally the case when automatic multirun welding is performed in the same conditions of welding current and energy as semi automatic welding with the concerned wire-gas combination.
![]()
156 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
2. Grades and marks
(1) The automatic welding consumables are classified as specified in Table 2.2.25.
Table 2.2.25 Grade and Marks
For normal strength steel | For higher strength steel | For steel for low temperature service |
1, 2, 3 | 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 | L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 |
(2) Automatic welding materials which have passed the tests for each welding process given in Table 2.2.28 are to be appended with the suffixes shown in Table 2.2.26 at the end of their marks.
(3) In the preceding (2), a suffix G will be added to the grade mark for gas shielded arc automatic welding consumables, and a suffix N will be added for self-shielded wire automatic welding consumables Further, the type of gas used is to be as specified in Table 2.2.27, and the suffix given in Table 2.2.27 will be added after the suffix G. (e.g. 3YTM G (M 1))
Table 2.2.26 Marks
Welding technique | Mark |
Multi-run technique(1) | M |
Two-run technique(2) | T |
Multi-run and two-run technique | TM |
NOTES: (1) Multi-run technique refers to a welding process involving multiple passes. (2) Two-run technique refers to a welding process involving a single pass on both sides. | |
Table 2.2.27 Kinds of Gas
Group | Type | (1)(2) | ||||||
M 11 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 Rest | ||||
M 12 | 1 | 5 | Rest | |||||
M 13 | 1 | 3 | Rest | |||||
M 14 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | Rest | |||
M 21 | 6 | 25 | Rest | |||||
M 2 | M 22 | 4 | 10 | Rest | ||||
M 23 | 6 | 25 | 1 | 8 | Rest | |||
M 31 | 26 | 50 | Rest | |||||
M 3 | M 32 | 11 | 15 | Rest | ||||
M 33 | 6 | 50 | 9 | 15 | Rest | |||
Gas composition (V ol.%)
M 1
C 1 100
C
C 2 Rest 1 30
I I 1 100
E E 1 Except above
NOTE:
(1) Argon may be substituted by Helium up to 95 % of the Argon content.
(2) Approval covers gas mixtures with equal or higher Helium contents only.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 157
![]()
3. General provisions for tests
(1) Steel plates to be used for test assemblies are to be as given in Table 2.2.28, appropriate to the kind of automatic welding consumables.
(2) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of test assemblies, grades and number of test
specimens to be taken from each test assembly for automatic welding consumables are to be as given in Table 2.2.29.
(3) For the approval of automatic welding consumables, the tests specified in the preceding (2) are
to be conducted for each brand of automatic welding
(4) For gas shielded arc automatic welding consumables,
consumables.
the test in the preceding (3) is to be per-
formed for each type of gas given in
recommends gas types of the group of
Table 2.2.27. When the manufacturer of the material
M 1, M 2, M 3 or C in Table 2.2.27 and the test is sat-
isfactorily conducted in accordance with the preceding (3) on one of the gas type, the test on
the other gas types belonging to the same group is allowed to be dispensed with at the dis- cretion of the Society.
(5) Unless otherwise agreed by the Society, additional approval tests are required when a shielding gas is used other than that used for the original approval tests.
(6) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the
range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met-
al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current
be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
(AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to
Table 2.2.28 Grades of Steel used for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumable | Grade of steel used for test assembly(1)(2) |
1 | A |
2 | A , B or D |
3 | A , B , D or E |
1Y | A H 32 or A H 36 |
2Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32 or D H 36 |
3Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32 or E H 36 |
4Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
5Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
2Y 40 | A H 40 or D H 40 |
3Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40 or E H 40 |
4Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
5Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
L 1 | E o r R L 235A |
L 2 | E , R L 235A , R L 235B , R L 325A or R L 325B |
L 3 | R L 325A , R L 325B or R L 360 |
L 91 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
L 92 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
NOTES: (1) Notwithstanding the requirements in this Table, normal strength steel or higher strength steels may be used for deposited metal test assembly In this case, test assemblies of grade L 91 and L 92 are to be appropriately buttered. (2) The tensile strength of higher strength steels A H 32, D H 32, E H 32 and FH 32 used in butt weld test assemblies is to be greater than 490 | |
![]()
158 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.29 Kinds of Test of Automatic Welding Consumables
Welding technique(7) | Kind of test(8) | Grade of welding consumables | Test assembly | Kinds and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||
Number | Dimen -sions | Thickness (mm)(3) | |||||
Multi-run technique | Deposited metal test | 1, 2, 3 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 | 1 | Fig 2.2.24 | 20 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Impact test specimen: 3 | |
Butt weld test | 1(4) | Fig 2.2.25 | 20~25 | Tensile test specimen: 2(4) Face bend test specimen: 2 (4)(6) Root bend test specimen: 2 (4)(6) Impact test specimen: 3 | |||
Two-run technique | Butt weld test | Submerged arc welding | 1, 1Y | 1 | Fig 2.2.26 | 12~15 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test speci- men: 1(5) Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 |
1 | 20~25 | ||||||
2, 3 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 | 1 | 20~25 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test speci- men: 1(5) Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | ||||
1 | 30~35 | ||||||
Gas shielded and self-shielded arc welding | 1, 2, 3 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 | 1 | 12~15(1) | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test speci- men: 1(5) Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | |||
20(2) | |||||||
1 | 20~25(1) | ||||||
acceptable maximum thickness( 2) | |||||||
Butt weld test | L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 | 1 | 12~15 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test speci- men: 1(5) Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | |||
1 | 20 or acceptable maximum thickness | ||||||
NOTES: (1) Thickness of test assemblies where applied maximum plate thickness is not more than 25 mm. (2) Thickness of test assemblies where applied maximum plate thickness is more than 25 mm. (3) Where thickness is restricted by welding process, thickness of test assemblies may be changed upon approval of the Society. Test assemblies shall then be welded using plates of 12 to 15 mm and 20 to 25 mm irrespective of the grade for which the approval is requested. (4) The number of butt weld test assemblies for multi-run gas shielded and self-shielded arc welding techniques is to be one for each welding position. However, where there is more than one welding position, the number of tensile test specimens and bend test specimens selected from the test assemblies for each welding position may be half of the specified number. (5) Test specimens are to be selected from only the thicker of two test assemblies. (6) The number of face bend and root bend test specimens selected from the butt weld test assemblies for L 91 and L 92 is to be one each. (7) Tests on both multi-run and two-run technique are to be conducted for multi-run and two-run welding re- spectively, and the number, dimensions and thickness of test assemblies, along with the grades and number of test specimens selected from each test assembly are to be according to each of the welding processes. However, the number of tensile test specimens in the deposited metal test for the multi-pass welding technique is to be one. (8) The hydrogen test may be applied by request of the manufacturer. (9) Where approval is requested for welding of both normal strength and higher strength steel two assemblies are to be prepared using higher strength steel. Two assemblies prepared using normal strength steel may also be required at the discretion of the Society. | |||||||
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 159
![]()
(7) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment.
(8) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as- certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
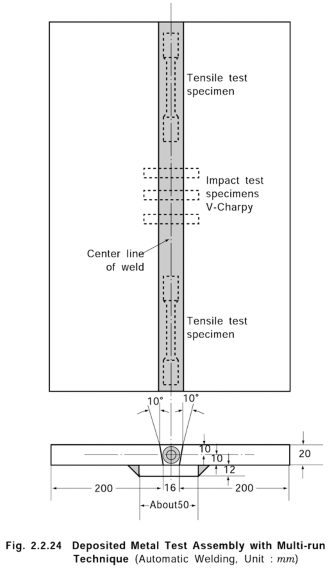
4. Deposited metal test with multi-run technique
(1) Welding of deposited metal test assemblies
(a) Test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.24 are to be welded in the flat position by multirun
technique according to the normal practice. The direction of deposition of each run is to alternate from each end of the plate. After completion of each run, the flux and welding slag is to be removed.
(b)
(c)
The thickness of layer is not to be less than the diameter of wire nor less than 4 mm whichever is the greater for submerged arc automatic welding consumables. For gas shield and self-shielded are automatic welding consumables the thickness of layer is not to be less than 3 mm.
![]()
![]()
After each run, the test assembly is to be left in still air until it has cooled to less than
250 but not below 100 , the temperature being taken at the centre of the weld on the
surface of seam.
(2) Chemical analysis
The chemical analysis of the deposited weld metal in each test assembly is to be supplied by
the manufacturer and is to include the content of all significant alloying element.
![]()
160 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(3) Deposited metal tensile test with multi-run technique
(a) The tensile test specimens, two from each test assembly, are to be machined to dimensions
R14A test specimen as shown in Table 2.2.1, care being taken that the longitudinal axis coincides with the centre of weld and the mid-thickness of plates.
(b)
The tensile strength, yield point and elongation of each test specimen are to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.30, where the upper limit of tensile strength is ex-
ceeded, special consideration will be given to the approval of the electrode, taking into con-
sideration of the other mechanical
composition of deposited metal.
properties shown in the
test results and the chemical
(c)
The tensile test specimens may be
![]()
subjected to a temperature not exceeding 250 for a
period not exceeding 16 hours for hydrogen removal prior to testing.
(4) Deposited metal impact test with multi-run technique
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di- mensions R 4 test specimen as shown in Table 2.1.3. The test specimen is to be cut with its longitudinal axis transverse to the direction of welding, and the test specimen is to co-
incide with the mid-thickness of the plate shown in Fig 2.2.19.
(b) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the
Table 2.2.30.
requirements given in
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.30 Tensile and Impact Test Requirements for Deposited Metal test
Grade of welding material | Tensile strength ( ) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation (%) | Impact test | |
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | ||||
1 | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | 20 | 34 min. |
2 | 0 | ||||
3 | -20 | ||||
1Y | 490 660 | 375 min. | 22 min. | 20 | |
2Y | 0 | ||||
3Y | -20 | ||||
4Y | -40 | ||||
5Y | -60 | ||||
2Y 40 | 510 690 | 400 min. | 22 min. | 0 | 39 min. |
3Y 40 | -20 | ||||
4Y 40 | -40 | ||||
5Y 40 | -60 | ||||
L 1 | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | -40 | 27 min. |
L 2 | 440 610 | 345 min. | 22 min. | -60 | |
L 3 | 490 660 | 375 min. | 21 min. | -60 | |
L 91 | 590 min. | 375 min.(1) | 25 min. | -196 | |
L 92 | 660 min. | 410 min.(1) | 25 min. | -196 | |
NOTE: (1) 0.2 % yield stress | |||||
(c) The notch is to be positioned in the centre of weld and is to be specimens perpendicular to the surface of plate.
(d) When the absorbed energy of two or more test specimens among a
![]()
![]()
cut in the face of test
set of test specimens is
less in value than the specified average absorbed
energy
or when
the absorbed energy of a
single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the the test is considered to have failed.
specified
average absorbed energy,
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 161
![]()
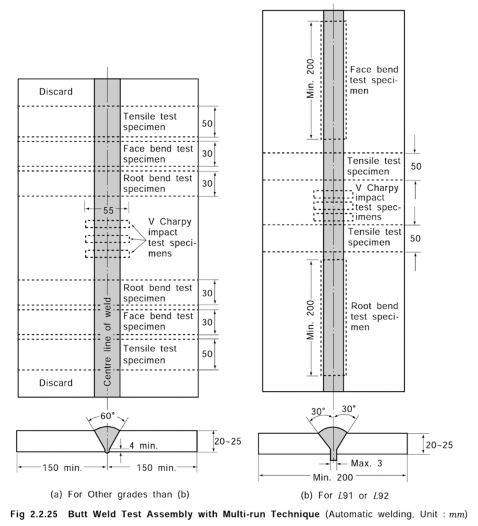
5. Butt weld test with multi-run technique
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies with multi-run technique
(a) The face side of the test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.25 is to be multi-pass welded in
flat position, preceding 4.
consumables,
and the corresponding welding procedure is to follow the requirements of the (1). However, for gas shield arc and self shielded arc wire automatic welding
the welding position is to be as specified by the manufacturer.
(b) After completing the face welding in downhand position, back welding is performed. In
this instance, back chipping may be carried out to expose sound deposited metal at the root.
(2) Butt weld tensile test with multi-run technique
(a) The tensile test specimens are to be prepared to R 2A specimen shown in Table 2.2.1 and
two test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly.
(b)
(c)
The surface of weld is to be machined flush with the surface of plate.
The tensile strength of test specimen is to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.31.
(3) Butt weld bend test with multi-run technique
(a) The face bend and root bend test specimens are to be R B 4 specimen shown in Table
2.2.2, and two test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly. However, for L 91 or L 92, the face bend and root bend specimens are to be R B 1 specimen shown in Table
![]()
2.2.2, and test specimens are to be taken longitudinally from each test assembly.
(b)
The test specimens are to be capable of withstanding, without crack exceeding 3 long on the outer surface of other defects, being bent through an angle of 120 degrees over a former having a radius of 1.5 tim es the thickness of test specimen. The radius and angle of the former for L 91 and L 92, however, are to be 2 tim es the thickness of the specimen and 180 degrees respectively.
![]()
162 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.31 Tensile and Impact Test Requirements for butt weld test with multi-run technique
Grade of welding material | Tensile strength( ) | Impact test | |
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | ||
1 | 400 min. | 20 | 34 min. |
2 | 0 | ||
3 | 20 | ||
1Y | 490 min. | 20 | |
2Y | 0 | ||
3Y | 20 | ||
4Y | 40 | ||
5Y | 60 | ||
2Y 40 | 510 min. | 0 | 39 min. |
3Y 40 | 20 | ||
4Y 40 | 40 | ||
5Y 40 | 60 | ||
L 1 | 400 min. | 40 | 27 min. |
L 2 | 440 min. | 60 | |
L 3 | 490 min. | 60 | |
L 91 | 630 min. | 196 | |
L 92 | 670 min. | 196 | |
![]()
(4) Butt weld impact test with multi-run technique
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di-
mensions R 4 test specimens as shown in Fig 2.1.3. The test specimen is to be cut with its longitudinal axis perpendicular to the direction of welding, and the test specimen is to
coincide with the mid-thickness of the plate shown in Fig 2.2.19.
(b) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.31.
(c)
The requirements in Par 4. (4), (c) and (d) are to correspondingly apply to this Paragraph.
6. Butt weld test with two-run technique
(1) Welding of Butt weld test assemblies with two-run technique
(a) Test assemblies are to be prepared as shown in Fig 2.2.26, and the diameter of wire and
edge preparation are to be as shown in Fig 2.2.27, but some deviation may be allowed where accepted by the Society.
(b) Test assemblies are to be welded according to the normal practice in downhand position by
![]()
two-run technique where each run is to be started alternately from each end of the plate. After completing the first run, the assembly is to be left in still air until it has cooled to
100 or below, the temperature being taken at the centre of weld on the surface of seam.
(2) Chemical analysis
The chemical analysis of the weld metal is to be supplied by the manufacturer, and is to in-
clude the content of all significant alloying elements.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 163
![]()


![]()
164 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(3) Butt weld tensile tests with two-run technique
(a) The tensile test specimens are to be R2A specimen shown in Table 2.2.1 and two test specimens are to be taken from each welded assembly.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
The surface of weld is to be machined flush with the surface of plate.
The tensile strength of test specimen is to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.31.
![]()
One longitudinal tensile test specimen of R14A shown in Table 2.2.1 is to be machined from the thicker of the test assembly specified in Table 2.2.28 and the longitudinal direc- tion of the test specimen is to be parallel to the weld line and the centre line of the test specimen is to coincide with the centre of second layer.
Tathuerelonnogtituedxcineaelditnegnsi2le50test sfoprecaimpeneriiondthneot perxeceeddiningg (146) hmouayrs bfoer shuybdjreocgteedn rteomoavatlempprieorr-
to testing.
The requirements of tensile test specified in the preceding (d) and (e) are to be as given in
Table 2.2.30. Where the upper limit of tensile strength is exceeded, special consideration
will be given to the approval of the welding consumables, taking into consideration of the other mechanical properties shown in the test results and the chemical composition of de- posited metal.
(4) Butt weld bend test with two-run technique
(a) The face and root bend test specimens are to be RB4 or RB5 specimen shown in Table
2.2.2 and test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly. However, for L91 and
L92, the face and root bend test specimens are to be RB1 test specimens and test speci- mens shown in Table 2.2.2 are to be taken longitudinally from each test assembly.
(b) The requirements in Par 5. (3), (b) are to correspondingly apply to this Paragraph.
(5) Butt weld impact test with two-run technique
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimens as shown in Table 2.1.3, and the
to di- longi-
tudinal direction of the test specimen is to be perpendicular to the weld line and the surface
of weld about 2 mm apart is to coincide with the surface of specimen as shown in Fig 2.2.28.
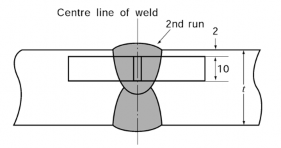
Fig 2.2.28 Position of impact Test Specimen for Butt Weld Test Assembly with Two-Run Technique (Unit : mm, t : plate thickness)
(b) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.31.
(c) The requirements in Par 4. (4), (c) and (d) are to correspondingly apply to this Paragraph.
7. Hydrogen test
The hydrogen test is to be in accordance with 602. 6 of the Rules
8. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspection, tests specified in the following (2) are to be conducted for each brand of the approved consumables, and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. involved in the annual inspections are to be as given in Table 2.2.32.
(3) The welding procedures and requirements for test assemblies of tests specified in the preceding
(2) are to be as specified in Pars 4 through 6.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 165
![]()
Table 2.2.32 Kinds of Test for Annual Inspection
Grade of welding consumables | Welding technique(1) | Kind of test | Test assembly | Kinds and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||
Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm) | |||||
1, 2, 3 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 | Multi-run technique | Deposited metal test | 1 | Fig 2.2.24 | 20 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | |
Two-run technique | Butt weld test | Submerged arc welding | 1 | Fig 2.2.26 | 20 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | |
Gas shielded and self shielded arc welding | 1 | 20~25 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend test specimen: 1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 | ||||
NOTE: (1) Tests on both multi-run and two run technique are to be conducted for multi-run and two run welding respectively. However, longitudinal tensile test of two run technique are not required. | |||||||
9. Changes in grades
(1) Where changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness of automatic welding con- sumables approved are to be made, tests specified in the following (2), (3) and (4) are to be carried out and satisfactorily passed in accordance with the requirements in 601. 6 (3).
(2) Changes in grades relating to the strength or toughness of multi-run automatic welding con- sumables are to be in accordance with the requirements in the following (a) and (b).
(a) For changes in the grades relating to strength, the butt weld tests, specified in the annual
inspection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
(b) For changes in the grades relating to toughness, the butt weld impact tests, specified in the annual inspection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
(3) Changes in grades relating to the strength or toughness of two-run automatic welding con-
sumables are to be in accordance with the requirements in the following (a) and (b).
(a) For changes in the grades relating to strength, all tests
conducted.
(b) For changes in the grades relating to toughness, the butt annual inspections of Par 8 and in the requirements
conducted.
(4) Changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness
specified in Par 3 (1) are to be
weld impact tests, specified in the of the preceding (a), are to be
of automatic welding consumables
for multi-run and two-run use are to be as specified in the preceding (2) and (3).
604. Semi-automatic welding consumables for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low temperature service
1. Application
Welding consumables for semi-automatic welding for normal and steels for low temperature service given in the following "semi-automatic welding consumables") are to be subjected spections in accordance with the requirements in 604.
(a) Gas shielded arc semi-automatic welding consumables(flux matic welding consumables with shielding gas)
strength steels, higher strength steels
(a) and (b) (hereinafter referred to as to the approval test and annual in-
cored wire and solid wire semi-auto-
(b) Self-shielded arc semi-automatic welding consumables(solid wire and flux cored matic welding consumables without shielding gas).
wire semi-auto-
![]()
166 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
2. Grades and marks
(1) The semi-automatic welding consumables are classified as specified in Table 2.2.33.
Table 2.2.33 Grades and Marks
For normal strength steel | For higher strength steel | For steel for low temperature service |
1, 2, 3 | 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y 5Y 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40 | L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 |
(2) A suffix "S" will be added after the grade mark to indicate approval for semi-automatic mul- ti- run welding. For wires intended for both semi-automatic and automatic welding, the suffixes will be added in combination.(eg. 3Y SM )
(3) A suffix G will be added to the grade marks for semi-automatic welding consumables which use shield gas, and a suffix N will be added for semi-automatic welding consumables which do not use shield gas. Further, the type of shield gas used is to be as specified in Table 2.2.24, and the suffix given in Table 2.2.24 will be added after the suffix G. (e.g. 3Y S G (M 1))
(4) For low hydrogen electrodes, which have passed the fixes given in Table 2.2.22 are to be added to electrode. (e.g. 3Y S H5)
3. General provisions for tests
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of
hydrogen test specified in 602. 6, the suf- the end of the grade marks of the said
test assemblies, diameter of wire used for
welding, welding position, grades and number of test specimens to be taken from each test as-
sembly, position for semi-automatic welding consumables used in butt welds or in both butt and
fillet welds are to be as given in Table 2.2.34.
(2) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of test assemblies, diameter of wire used for
welding, welding position, grades and number of test specimens to be taken from each test as- sembly for semi-automatic welding materials used in fillet welds only are to be as given in
Table 2.2.18.
(3) Steel plates to be used for test assemblies are to be as given in Table 2.2.35, appropriate to the kind of semi-automatic welding consumables.
(4) For the approval of semi-automatic welding consumables, the test specified in the preceding (1)
and (2) are to be conducted for each brand of semi-automatic welding consumables.
(5) For semi-automatic welding consumables, the test in the preceding (4) is to be performed for
each type of gas types of
conducted in
gas given in Table 2.2.27. When the manufacturer of the material recommends the group of M 1, M 2, M 3 or C in Table 2.2.27 and the test is satisfactorily
accordance with the preceding (3) on one of the gas type, the test on the other
gas types belonging to the same group is allowed to be dispensed with at the discretion of the
Society.
(6) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met- al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
(7) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment.
(8) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as-
certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 167
![]()
Table 2.2.34 Kinds of Test for Semi-automatic Welding Consumables
Kind of test(8) | Test assembly | Kinds and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||||
Welding position | Wire diameter (mm) | Number | Dimen- sions | Thicknes s (mm) | ||
Deposited metal test | Flat | maximum diameter | 1(1) | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3 |
minimum diameter | 1(1) | |||||
Butt weld test | Flat | First-run: minimum diameter Remaining-run: maximum diameter(4) | 1(2) | Fig 2.2.20 | 15~20 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend test specimen :1 Root bend test specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3(3) |
Horizontal(5) | 1 | |||||
Vertical upward | 1 | |||||
Vertical downward | 1 | |||||
Overhead | 1 | |||||
Fillet weld test(6) | Horizontal | One side: maximum diameter The other side: minimum diameter | 1 | Fig 2.2.21 | 20 | Macro test specimen: 3(7) Hardness test specimen: 3(7) Fracture test specimen: 2 |
NOTES: (1) Where the core diameter to be manufactured is of single variety, the number of test assembly is to be one. (2) Where tests are conducted solely in the Flat position. one test assembly welded with wire of different diameters is to be added. Where only one diameter is manufactured, only one deposited metal assembly is to be prepared. (3) Impact tests are not required for welding in overhead position. (4) The butt weld assemblies in positions other than downhand, are to be welded using, for the first run, wire of the smallest diameter to be approved, and, for the remaining runs, the largest diameter of wire recommended by the manufacturer for the position concerned. (5) For semi-automatic welding consumables which have passed butt weld tests in the downhand and verti- cal upward positions, the horizontal butt weld test may be omitted. at the discretion of the Society. (6) This test is to be added solely against welding consumables for use in both butt and fillet weld. (7) The test specimens used in the macro-etching test and hardness test are to be the same. (8) For low hydrogen welding consumables, an hydrogen test may be conducted by the application of the manufacturer, and test assembly is to be as specified in 602. 6 (1). | ||||||
![]()
168 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.35 Grades of Steel for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumables | Grade of steel for test assembly (1)(2) |
1S | A |
2S | A , B or D |
3S | A , B , D or E |
1YS | A H 32 or A H 36 |
2YS | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32 or D H 36 |
3YS | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32 or E H 36 |
4YS | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
5YS | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
2Y 40S | A H 40 or D H 40 |
3Y 40S | A H 40, D H 40 or E H 40 |
4Y 40S | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
5Y 40S | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
L 1S | E o r R L 235A |
L 2S | E , R L 235A , R L 235B , R L 325A or R L 325B |
L 3S | R L 325A , R L 325B or R L 360 |
L 91S | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
L 92S | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
NOTES; (1) Notwithstanding the requirements in this Table, normal or higher strength steels may be used for deposited metal test assembly. In this case, test assemblies of grade L 91 and L 92 are to be ap- propriately buttered. (2) The tensile strength of higher strength steels A H 32, D H 32, E H 32 and F H 32 used in butt weld test assemblies is to be greater than 490 . | |
![]()
4. Deposited metal test
(1) Welding of Deposited metal test assemblies
(a) Test assembly as shown in Fig 2.2.18 is to be welded in the flat normal practice.
position according to the
(b) Test assembly is to be welded in single or multi-run layers, and the direction of deposition of each run is to alternate from each end of the plate, each run of weld metal being not
![]()
![]()
less than 2 mm but not more than 6 mm thick.
(c)
A25f0ter eabcuht rnuont, tbheelotwest 1a0s0sem,bltyheis tetombperalteufrte ibneinsgtilltakaeirn uant titlheitcehnatsre coofoltehde
surface of seam.
twoeldlesosn ththaen
(2) Chemical analysis
The chemical analysis of the deposited weld metal in each test assembly is to be supplied by
the manufacturer and is to include the content of all significant alloying element.
(3) Deposited metal tensile test
(a) The tensile test specimen, one from each test assembly, is to be machined to dimensions
R14A test specimen as shown in Table 2.2.1, care being taken that the coincides with the centre of weld and the mid-thickness of plates.
(b) The tensile test specimen may be subjected to a temperature not exceeding riod not exceeding 16 hours for hydrogen removal prior to testing.
longitudinal axis
![]()
250 for a pe-
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 169
![]()
(c) The tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of each test specimen are to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.36, where the upper limit of tensile strength is ex- ceeded, special consideration will be given to the approval of the electrode, taking into con-
sideration of the other mechanical properties shown in the test results composition of deposited metal.
and the chemical
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.36 Tensile and Impact Test Requirements for Deposited Metal test
Grade of welding consumables | Tensile strength ( ) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation ( ) | Impact test | |
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | ||||
1S | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | 20 | 47 min. |
2S | 0 | ||||
3S | 20 | ||||
1YS | 490 660 | 375 min. | 22 min. | 20 | |
2YS | 0 | ||||
3Y S | 20 | ||||
4YS | 40 | ||||
5YS | 60 | ||||
2Y 40S | 510 690 | 400 min. | 22 min. | 0 | |
3Y 40S | 20 | ||||
4Y 40S | 40 | ||||
5Y 40S | 60 | ||||
L 1S | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | 40 | 34 min. |
L 2S | 440 610 | 345 min. | 22 min. | 60 | |
L 3S | 490 660 | 375 min. | 21 min. | 60 | |
L 91S | 590 min | 375 min.(1) | 25 min. | 196 | 27 min. |
L 92S | 660 min | 410 min.(1) | 25 min. | 196 | |
NOTE: (1) 0.2 % yield stress | |||||
![]()
![]()
![]()
(4) Deposited metal impact tests
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di-
mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimens as shown in Table 2.1.3. The test
speci-
men is to be cut with its longitudinal axis transverse to the direction of welding, and the test specimen is to coincide with the mid-thickness of the plate shown in Fig 2.2.21.
(b) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.36.
(c)
(d)
The notch is to be positioned in the centre of weld and is to be cut in the face of test specimens perpendicular to the surface of plate.
When the absorbed energy of two or more test specimens among a set of test specimens is
less in value than the specified average absorbed energy or when the absorbed energy of a single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the specified average absorbed energy, the test is considered to have failed.
![]()
170 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
5. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies
(a) Test assembly as shown in Fig 2.2.20 is to be welded in each welding position (flat, hori- zontal-
vertical, vertical-upward, vertical-downward and overhead) which is recommended by the manufacturer.
![]()
![]()
(b) A25f0ter eabcuht nruont , btehleowtes1t00asse,mtbhley teismptoerabteurelefbteiinng stailkl enairatunthtiel ictenhtares
surface of seam.
(2) Butt weld tensile tests
cooled to less than of the weld on the
(a) The tensile test specimen is to be R 2A test specimen shown in Table 2.2.1 and the test
(b)
(c)
specimen is The surface
The tensile
2.2.37.
to be taken from each test assembly.
of weld is to be machined flush with the surface of plate.
strength of test specimen is to comply with the requirements given in Table
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.37 Tensile and Impact Test Requirements for Butt weld test
Grade of welding consumables | Tensile strength ( ) | Impact test | ||
Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | |||
Flat, Horizontal Overhead | Vertical upward, Vertical downward | |||
1S | 400 min. | 20 | 47 min. | 34 min. |
2S | 0 | |||
3S | 20 | |||
1Y S | 490 min. | 20 | ||
2Y S | 0 | |||
3Y S | 20 | |||
4Y S | 40 | |||
5Y S | 60 | |||
2Y40S | 510 min. | 0 | 39 min. | |
3Y40S | 20 | |||
4Y40S | 40 | |||
5Y40S | 60 | |||
L 1S | 400 min. | 40 | 27 min. | 27 min. |
L 2S | 440 min. | 60 | ||
L 3S | 490 min. | 60 | ||
L 91S | 630 min. | 196 | ||
L 92S | 670 min. | 196 | ||
![]()
(3) Butt weld bend test
(a) The face and root bend test specimens are to be RB4 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2, and
test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly. However, for L 91 or L 92,
the
(b)
face and root bend specimens are to be RB1 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2, and test specimens are to be taken longitudinally from each test assembly.
The test specimens are to be capable of withstanding, without crack exceeding 3 mm long on the outer surface of other defects, being bent through an angle of 120 degrees over a former having a radius of 1.5 times the thickness of test specimen. The radius and angle of the former for L 91 and L 92, however, are to be 2 times the thickness of the specimen and 180 degrees respectively.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 171
![]()
(4) Butt weld Impact test
(a) One set of three impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di-
mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimens as shown in Table 2.1.3. The test speci- men is to be cut with its longitudinal axis transverse to the direction of welding, and the
test specimen is to coincide with the mid-thickness of the plate shown in Fig 2.2.19.
(b)
(c)
Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.37.
The requirements in Par 4 (4), (c) and (d) are to correspondingly apply to this Paragraph.
6. Fillet weld test assemblies
(1) Welding of fillet weld test assemblies The test assemblies are to be in accordance with the re- quirements in 602. 7 (1).
(2) Fillet weld macro-structure test The macro-structure test is to be correspondingly in accord-
ance with the requirements in 602. 7 (2).
(3) Fillet weld hardness test The hardness test is to be correspondingly in accordance with the re- quirements in 602. 7 (3).
(4) Fillet weld fracture test The fracture test is to be correspondingly in accordance with the re-
quirements in 602. 7 (4).
7. Hydrogen test
Flux-cored or flux-coated wires which have satisfied the requirements for Grades 2S, 2YS, 2Y40S, 3S, 3YS, 3Y40S, 4YS or 4Y40S may, at manufacturer's option, be submitted to the hydrogen test as detailed in 602. 6. using the manufacturer's recommended welding conditions and adjusting the deposition rate to give a weight of weld deposit per sample similar to that deposited when using manual electrodes.
8. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspections, tests specified in the following (2) are to be conducted for each brand of the approved consumables, and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspection are to be as given in Table 2.2.38.
Table 2.2.38 Kind of Test for Annual Inspection
Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||||
Welding position | Diameter of wire (mm) | Num ber | Dimension | Thickness (mm) | |||
Deposited metal test | Flat | (1) | 1 | Fig 2.2.18 | 20 | Tensile test specimen : 1 Impact test specimen : 3 | |
NOTE: (1) The diameters of the wire are to be within the range specified by the manufacturers. | |||||||
(3) The welding procedures and requirements for test assemblies of tests specified in the preceding
(2) are to be as specified in Par 4.
9. Changes in grades
(1) Where changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness of welding consumables ap- proved are to be made, tests specified in the following (2) and (3) are to be carried out and satisfactorily passed in accordance with the requirements in 601. 6 (3).
(2) For changes in the grades relating to strength, the butt weld tests, specified in the annual in- spection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
(3) For changes in the grades relating to toughness, the butt weld impact tests, specified in the an-
nual inspection of Par 8 and in the requirements of Par 3 (1), are to be conducted.
![]()
172 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
605. Electro-slag and electro-gas welding consumables
1. Application
Electro-slag and electro-gas welding consumables for normal strength and higher strength steels (hereinafter referred to as "welding consumables") are to be in accordance with the requirements in 605.
2. Grades and marks
Welding consumables are classified as specified in Table 2.2.39.
Table 2.2.39 Grades and Marks
For normal strength steel | For higher strength steel |
1V , 2V , 3V | 1Y V , 2Y V , 3Y V , 4Y V , 5Y V 2Y 40V , 3Y 40V , 4Y 40V , 5Y 40V |
3. General provisions for tests
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of test assemblies, grades and number of test
specimens to be taken from each test assembly for welding consumables are to be as given in
Table 2.2.40.
Table 2.2.40 Kinds of Test for Electro-Slag and Electro-Gas Welding Consumables
Kind of test | Test assembly(1) | Kinds and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||
Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm)(2) | ||
Butt weld test | 1 | Fig 2.2.29 | 20 ~ 25 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 2 Side bend test specimen: 2 Impact test specimen: 6 Macro structure test specimen: 2 |
1 | 35 ~ 40 | |||
NOTE: (1) Where approval is requested for welding of both normal strength and higher strength steel two assem- blies are to be prepared using higher strength steel. Two assemblies prepared using normal strength steel may also be required at the discretion of each Classification Society. (2) Where thickness is restricted by welding process, thickness of test assemblies may be changed upon approval of the Society. In this case, the maximum test thickness is to be taken as the maximum applicable thickness. | ||||
(2) Steel plates to be used for test assemblies are to be as given in Table 2.2.41, appropriate to the kind of welding consumables.
(3) For the approval of welding consumables, the tests specified in the preceding (1) are to be con- ducted for each brand of welding consumables.
(4) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the
range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met- al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to
be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
(5) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment.
(6) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as- certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 173
![]()
Table 2.2.41 Grades of Steel used for Test Assembly
Grade of welding material | Grade of steel used for test assembly (1)(2) |
1V | A |
2V | A , B or D |
3V | A , B , D or E |
1Y V | A H 32 or A H 36 |
2Y V | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32 or D H 36 |
3Y V | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32 or E H 36 |
4Y V | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
5Y V | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
2Y40V | A H 40 or D H 40 |
3Y40V | A H 40, D H 40 or E H 40 |
4Y40V | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
5Y40V | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
NOTE: (1) The tensile strength of higher strength steels of A H 32, D H 32, E H 32 and F H 32 used in the test assemblies is to be greater than 490 . (2) This is in respect of the content of grain refining elements, and if general approval is required, a niobium treated steel is to be used for the approval tests. | |
![]()
4. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies
(a) Test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.29 are to be welded upward in vertical position in one Pass.
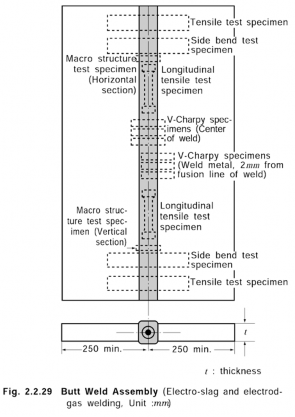
![]()
174 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(b) The welding conditions and edge preparation are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer.
(2) Tensile test
(a) Two tensile test specimens to be R2A specimen and two longitudinal tensile test specimens to be R14A specimen as shown in Table 2.2.1 are to be taken from each test assembly.
![]()
The longitudinal axis of test specimen coincides with the centre of weld and the mid-thick- ness of plates.
(b)
(c)
T25h0e lonfgoirtuadinpaelriotednsniolet teexscteesdpiencgim1e6nshomuarys fboer shuybdjerocgteedn troemthoevahlepatriotrreatotmteensttinngo.t exceeding
Tensile strength of each test specimen R2A and tensile strength, yield strength and elonga- tion of each longitudinal test specimen R14A are to comply with the requirements in Table
2.2.42. Where the upper limit of tensile strength is exceeded, special consideration will be
given to the approval of the welding consumables, taking mechanical properties shown in the test results and chemical
into consideration of the other composition of deposited metal.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.42 Tensile and Impact Test Requirements for Butt weld test
Grade of welding consumables | Tensile strength ( ) | Longitudinal Tensile Test | Impact test | |||
Tensile strength ( ) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation ( ) | Test temp. ( ) | Average absorbed energy (J) | ||
1V | 400 min. | 400 560 | 305 min. | 22 min. | 20 | 34 min. |
2V | 0 | |||||
3V | -20 | |||||
1YV | 490 min. | 490 660 | 375 min. | 22 min. | 20 | |
2YV | 0 | |||||
3YV | -20 | |||||
4YV | -40 | |||||
5YV | -60 | |||||
2Y40V | 510 min. | 510 690 | 400 min. | 22 min. | 0 | 39 min. |
3Y40V | -20 | |||||
4Y40V | -40 | |||||
5Y40V | -60 | |||||
![]()
![]()
(3) Bend test
(a) Bend test specimens are to be R B 6 specimens shown in Table 2.2.2
test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly.
and two side bend
(b) The test specimens are to be capable of withstanding, without crack exceeding 3 mm long
on the outer surface of other defects, being bent through an angle of 180 degrees over a former having a radius of two times the thickness of test specimen.
(4) Impact test
(a) Two sets of six impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di- mensions charphy V-notch impact test specimens as shown in Table 2.1.3 and the longi- tudinal direction of the test specimen is to be perpendicular to the weld line and the surface
of weld about 2 mm apart is to coincide with the surface of specimen as shown in Fig 2.2.30.
(b) The position of the notch is to be in accordance with Fig 2.2.30 (a) and (b) respectively, and its longitudinal direction is to be perpendicular to the surface of the test assembly.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 175
![]()
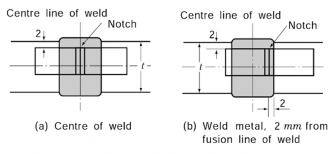
Fig 2.2.30 Position of Impact Specimen (Unit : mm, t = Plate thickness)
(c) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.42.
(d) When the absorbed energy of two or more test specimens among a set of test specimens is less in value than the specified average absorbed energy or when the absorbed energy of a single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the specified average absorbed energy, the test is considered to have failed.
(5) Macro-structure test
(a) Two macro-structure test specimens are to be taken from the position shown in Fig 2.2.29.
As for the surface to be tested, one is to be normal to the assembly surface and the other parallel to the assembly surface.
(b) Both the welded parts and the weld boundaries are to show complete fusion, penetration and sound metallurgical structure.
5. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspection, tests specified in the following (2) are to be conducted for each brand of the approved materials, and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspections are to be as given in Table 2.2.43.
(3) The welding procedures and requirements for test assemblies of tests specified in the preceding
(2) are to be as specified in Par 4.
Table 2.2.43 Kind of Test for Annual Inspection
Kind of test | Test assembly | Kinds and no. of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||
Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm)(1) | ||
Butt weld test | 1 | Fig 2.2.29 | 20 ~ 25 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal Tensile test specimen: 1 Side bend test specimen: 2 Impact test specimen: 6(1) |
NOTE: (1) One set of three impact test specimens may be taken from the centre of welded part. where approved by the Society. | ||||
6. Changes in grades
Where changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness of welding consumables approved are to be made, tests specified in Par 3 (1) are to be conducted and satisfactorily passed in ac- cordance with the requirements in 601. 6 (3).
![]()
176 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
606. One side welding and steels for low
1. Application
consumables for normal strength steels, higher strength steels temperature service.
(1) Welding consumables for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low tem- perature service given in the following (a) through (c) (hereinafter referred to as "one side auto- matic welding consumables") are to be subjected to the approval tests and annual inspections in accordance with the requirements in 606.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Submerged arc one side automatic welding consumables
Gas shielded arc one side automatic welding consumables (solid wire or flux cored wire with shielding gas)
Self-shielded arc one side automatic welding consumables (flux cored wire or flux coated wire without shielding gas)
![]()
![]()
(2) Approval tests and annual inspections of one side covered electrodes for normal strength steels, higher strength steels and steels for low temperature service, and one side semi-automatic weld- ing consumables are to be as deemed appropriate by the Society. See Guidance
![]()
![]()
(3) Approval tests and annual inspections for one side automatic welding consumables of muitiple electrodes are to be as deemed appropriate by the Society. See Guidance
2. Grades and marks
(1) One side automatic welding consumables are classified as specified in 603. 2. Further, one side automatic welding consumables which have passed the tests for each welding procedure given in Table 2.2.45 are to be appended with the suffixes given in Table 2.2.44 at the end of their marks.
(2) In the preceding (1), a suffix G will be added to the grade mark for gas shielded arc one side
automatic welding consumables, automatic welding consumables.
2.2.27 and the suffix given in
G (M 1))
and a suffix N will be added for self-shielded wire one side Further, the type of gas used is to be as specified in Table Table 2.2.27 will be added after the suffix G. (e.g. 3Y S M R
Table 2.2.44 Marks
Welding technique(1) | Marks |
One-run technique | SR |
Multi-run technique | M R |
One-run and multi-run technique | SM R |
NOTE: (1) One-run or multi-run technique refers to a welding process which performed in one pass or multiple passes respectively regardless of the number of electrodes. | |
3. General provisions for tests
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of test assemblies, grades and number of test specimens to be taken from each test assembly for one side automatic welding consumables are to be as given in Table 2.2.45.
(2) Steel plates to be used for test assemblies are to be as given in Table 2.2.46.
(3) For the approval of one side automatic welding consumables, the tests specified in the preceding
(1) are to be conducted for each brand of one side automatic welding consumables.
(4) For gas shield arc one side automatic welding consumables, the test in the preceding (3) is to be performed for each type of gas given in Table 2.2.27. When the manufacturer of the ma-
terial recommends gas types of the group of M 1, M 2, M 3 or C in Table 2.2.27 and the test is satisfactorily conducted in accordance with the preceding (3) on one of the gas type, the test on
the other gas types belonging to the same group is allowed to be dispensed with at the dis- cretion of the Society.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 177
![]()
Table 2.2.45 Kinds of Test for One-side Automatic Welding Consumables
Grade of welding consumables | Welding technique | Kind of test(4) | Test assembly | Kind and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||
Number | Thickness (mm)(1) | Dimension | ||||
1, 2, 3, 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y , 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40, L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 | One-run technique | Butt weld test | 1 | 12 ~ 15 | Fig 2.2.31 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 6 Macro-structure test specimen: 1 |
1 | Maximum thickness | |||||
Multi-run technique | 1 | 15 ~ 25 | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen :1 Root bend Specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 6 Macro-structure test specimen: 1 | |||
1 | 35 | |||||
One-run and Multi-run technique | 1 | Maximum thickness(2) | Tensile test specimen: 2 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 6 Macro-structure test specimen: 1 | |||
1 | 35(3) | |||||
NOTES: (1) Where thickness is restricted by welding process, thickness of test assemblies may be changed upon ap- proval of the Society. In this case, the maximum test thickness is to be taken as the maximum appli- cable thickness. (2) Thickness of test assembly for one run technique. (3) Thickness of test assembly for multi-run technique. (4) The hydrogen test may be carried out according to the manufacturer's request. | ||||||
![]()
178 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.46 Grades of Steel used for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumables | Grade of steel used for test assembly (1) |
1 | A |
2 | A , B or D |
3 | A , B , D or E |
1Y | A H 32 or A H 36 |
2Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32 or D H 36 |
3Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32 or E H 36 |
4Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
5Y | A H 32, A H 36, D H 32, D H 36, E H 32, E H 36, F H 32 or F H 36 |
2Y 40 | A H 40 or D H 40 |
3Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40 or E H 40 |
4Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
5Y 40 | A H 40, D H 40, E H 40 or F H 40 |
L 1 | E o r R L 235A |
L 2 | E , R L 235A , R L 235B , R L 325A or R L 325B |
L 3 | R L 325A , R L 325B or R L 360 |
L 91 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
L 92 | R L 9N 520 or R L 9N 590 |
NOTE: (1) The tensile strength of higher strength steels A H 32, D H 32, E H 32 and F H 32 used in the test as- semblies is to be greater than 490 N/mm 2 | |
(5) The combination of one side automatic welding materials are classified
2.2.47, appropriate to the welding procedure.
as given in Table
Table 2.2.47 Combinations of One Side Automatic Welding Consumables
Welding technique | Combinations of welding consumables |
Submerged one side automatic welding | Wire + Flux + Iron powder + Backing |
Gas shielded arc one side automatic welding | Wire + Gas + Iron powder + Backing |
Self-shielded arc one side automatic welding | Wire + Iron powder + Backing |
NOTE: Where iron powder is not used, iron powder is excluded in this Table. | |
(6) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met- al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
(7) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment.
(8) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as-
certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 179
![]()
4. Butt weld test assemblies with one-run and multi-run technique
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies with one-run and multi-run technique
(a) Test assemblies are to be prepared as shown in Fig 2.2.31, and the diameter of wire, root
gap and edge preparation are to be within the range specified by the manufacturer.
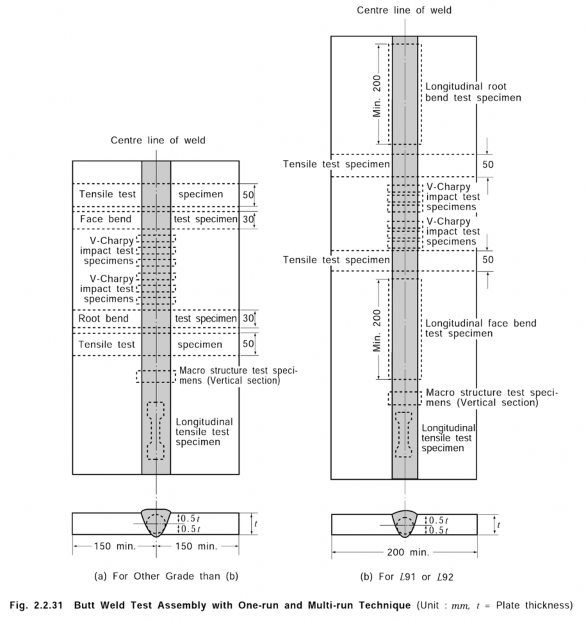
![]()
![]()
(b) Test assemblies are to be welded in downhand position by one-run technique or multi-run technique according to the procedures specified by the manufacturer. However, for gas shield and self-shielded arc one side automatic welding consumables, the welding position is to be specified by the manufacturer.
(c)
Alefstserthcaonmp2l5e0ting ebaucthnroutn btehleowtest10a0ssem, bthlye tiesmtpoerabteurelefbteiinng statikllenaiart uthnetilceint trheasofcowoelledd otno
the surface of seam.
(2) Butt weld tensile test with one-run and multi-run technique
(a) Tow tensile test specimens to be R 2A specimen and one longitudinal tensile test specimen to be R 14A specimen as shown in Table 2.2.1 are to be taken from each test assembly. The longitudinal axis of test specimen coincides with the centre of weld and the mid-thick-
![]()
180 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
ness of plate.
(b)
T0 he
flonr gaitupdeirniaold tneontsileexcteesdt inspgec1i6mehnoumrsayforbehysdurbojgeecntedremtoovaal tepmripoerratoturtestninogt . exceeding 25
(c)
Tensile strength of each test specimen R 2A is to comply with the requirements in Table
2.2.31. Tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of longitudinal tensile test specimens
R 14 are to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.30. Where the upper limit
of tensile strength is exceeded, special consideration will be given to the approval of the welding consumables, taking into consideration of the other mechanical properties shown in
the test results and chemical composition of deposited metal.
(3) Butt weld bend test with one-run and multi-run technique The bend tests are to comply with the requirements in 603. 6. (4).
(4) Butt weld impact test with one-run and multi-run technique
(a) Two sets of impact test specimens, from each test assembly, are to be machined to di- mensions R 4 test specimen as shown in Table 2.1.3. Longitudinal direction of the test
specimen is to be perpendicular to the weld line as shown in Fig 2.2.32.
(b) Test temperature and average absorbed energy are to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.31.
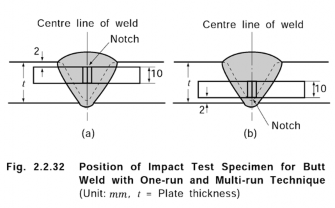
(c) The notch is to be positioned in the specimens perpendicular to the surface
centre of weld and is to be cut in the face of test of plate.
(d)
When the absorbed energy of two or
more test specimens among a set of test specimens
is less in value than the specified average absorbed energy or when the absorbed energy of a single test specimen is less in value than 70 % of the specified average absorbed energy,
the test is considered to have failed.
(5) Butt weld macro-structure test with one-run and multirun technique
(a) Macro-structure test specimens are to be taken from the position shown in Fig 2.2.31. The surface to be tested is to be perpendicular to the surface of the test assembly.
(b)
Both the welded parts and the weld boundaries are to show complete fusion, penetration and
sound metallurgical structure.
5. Hydrogen test
The hydrogen test is to be in accordance with 602. 6 of the Rules
6. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspection, tests specified in the following (2) are to be conducted for each brand of the approved consumables, and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspection are to be as given in Table 2.2.48.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 181
![]()
Table 2.2.48 Kinds of Test for Annual Inspection
Grade of welding consumables | Welding technique | Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | ||
Num ber | Dimension | Thickness (mm)(1) | ||||
1, 2, 3, 1Y , 2Y , 3Y , 4Y , 5Y , 2Y 40, 3Y 40, 4Y 40, 5Y 40, L 1, L 2, L 3, L 91, L 92 | One-run technique | Butt weld test(2) | 1 | Fig 2.2.31 | 20 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3(3) |
Multi-run technique | 1 | 20~25 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 Impact test specimen: 3(3) | |||
One-run and Multi-run technique | 1 | 20~25 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 Impact test Specimen: 3(3) | |||
NOTES: (1) Where the thickness of test assemblies is changed according to Note (1) of Table 2.2.45, the maximum test thickness for approval test is to be applied. (2) The butt weld tests for one-run and multi-run technique are to be carried out by one-run technique. (3) The positions of notch and selection of impact test specimens are to be as given in Fig2.2.32 (b). | ||||||
(3) The welding procedures and requirements of be as specified in Par 4.
7. Changes in grades
test assemblies for tests in the preceding (2) are to
Where changes in the grades relating to the strength or toughness of one side automatic welding consumables approved are to be made, all the tests specified in Par 3 (1) are to be carried out and satisfactorily passed in accordance with the requirements in 601. 6 (3).
607. Welding consumables for stainless steel
1. Application
(1) Welding consumables for stainless steels specified in Ch 1, Sec 3 (hereinafter referred to as "welding consumables") are to be subjected to the approval tests and annual inspections in ac- cordance with the requirements in 607.
![]()
![]()
(2) Welding consumables for duplex stainless steel is to be in accordance with the Guidance in re- lating to Rules. See Guidance
2. Grades and marks
(1) Welding consumables are classified as specified in Table 2.2.49.
(2) Submerged arc welding consumables which have passed the tests for each welding process given
in Table 2.2.51 are to be appended with the suffixes shown in Table 2.2.50 at the end of their marks.
(3) For flux cored wire semi-automatic welding consumables in the preceding (1), a suffix G will
be added to the grade mark for welding consumables which use shield gas, and a suffix N will
be added to the type of
the grade marks shield gas used
for welding consumables which do not used shield gas. Further, is to be as specified in Table 2.2.27 and the suffix given in
![]()
182 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.27 will be added after the suffix G. (e.g. R W 308G (C))
Table 2.2.49 Grades and Marks of Welding Consumables
Electrode for manual arc welding | Material for TIG and MIG welding | Flux cored wire semi-automatic welding | Consumables for submerged welding |
RD 308 | RY 308 | RW 308 | RU 308 |
RD 308L | RY 308L | RW 308L | RU 308L |
RD 309 | RY 309 | RW 309 | RU 309 |
RD 309L | RY 309L | RW 309L | - |
RD 309M o | RY 309M o | RW 309M o | RU 309M o |
RD 309M oL | - | RW 309M oL | - |
RD 310 | RY 310 | RW 310 | RU 310 |
- | RY 310S | - | - |
RD 310M o | - | - | - |
RD 316 | RY 316 | RW 316 | RU 316 |
RD 316L | RY 316L | RW 316L | RU 316L |
RD 317 | RY 317 | RW 317 | RU 317 |
RD 317L | RY 317L | RW 317L | RU 317L |
- | RY 321 | - | - |
RD 347 | RY 347 | RW 347 | RU 347 |
Table 2.2.50 Marks
Welding technique | Marks |
Multi-run technique | M |
Two-run technique | T |
Multi-run and Two-run technique | TM |
3. General provisions for tests
![]()
![]()
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of test assemblies, diameter of wire used for welding, grades and number of test specimens to be taken from each test assembly in each welding position for welding consumables are to be as given in Table 2.2.51. However, addi- tional tests appropriate to steels, such as test on corrosion-resistance test, impact test, macro etching test, etc., except the test given in Table 2.2.51 may be required where deemed neces- sary by the Society. See Guidance
(2) Steel plates to be used for test assemblies are to be as given in Table 2.2.52 according to the grades of welding consumables.
(3) For the approval of welding consumables, the tests specified in the preceding (1) are to be con- ducted for each brand of welding consumables.
(4) For flux cored wire semi-automatic welding materials, which use shield gas, the test in the pre- ceding (3) is to be performed for each type of gas given in Table 2.2.27. When the manu-
facturer of the consumables recommends gas types of the group of M 1, M 2, M 3 or C in
Table 2.2.27 and the test is satisfactorily conducted in accordance with the preceding (3) on one of the gas type, the test on the other gas types belonging to the same group is allowed to be dispensed with at the discretion of the Society.
(5) The welding conditions used such as amperage, voltage, travel speed, etc. are to be within the range recommended by the manufacturer for normal good welding practice. Where a filler met- al is stated to be suitable for both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), AC is to be used for the preparation of the test assemblies.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 183
![]()
Table 2.2.51 Kinds of Test of Welding Consumables for Stainless Steel
Kind of welding consumables | Kind of test | Test assembly | Kind and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||||
Thick- ness (mm) | No. | Welding position | Dia. of electrode or wire (1) (mm) | Dimen- sion | ||||
Electrode for manual arc welding | Deposited metal test | 12 | 1 | Flat | 3.2 | Fig 2.2.33 | Tensile test specimen: 1 | |
20 | 1 | 4.0 | ||||||
Butt weld test | 15~20 | 1 | Flat | 3.2 or 4.0 | Fig 2.2.34 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend Specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||
1 | Horizontal | |||||||
1 | Vertical upward | |||||||
1 | Vertical downward | |||||||
1 | Overhead | |||||||
Consumables for TIG welding | Deposited metal test | 12 | 1 | Flat | 2.4 | Fig 2.2.33 | Tensile test specimen: 1 | |
20 | 1 | 3.2 | ||||||
Butt weld test | 15~20 | 1 | Flat | 2.0~3.2 | Fig 2.2.34 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||
1 | Horizontal | |||||||
1 | Vertical upward | |||||||
1 | Vertical downward | |||||||
1 | Overhead | |||||||
Consumables for MIG welding | Deposited metal test | 12 | 1 | Flat | 1.2 | Fig 2.2.33 | Tensile test specimen: 1 | |
20 | 1 | 1.6 | ||||||
Butt weld test | 15~20 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~2.0 | Fig 2.2.34 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||
Horizontal | ||||||||
Vertical upward | ||||||||
Vertical downward | ||||||||
Overhead | ||||||||
Flux cored wire for semi-automatic welding | Deposited metal test | 12 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~2.4 | Fig 2.2.33 | Tensile test specimen: 1 | |
20 | 1 | 3.2 or max. dia | ||||||
Butt weld test | 15~20 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~3.2 | Fig 2.2.34 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||
Horizontal | ||||||||
Vertical upward | ||||||||
Vertical downward | ||||||||
Overhead | ||||||||
Consum- ables for sub- merged arc welding (2) | Multi-run technique | Deposited metal test | 19~25 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~4.0 | Fig 2.2.33 | Tensile test specimen: 1 |
Butt weld test | 19 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~4.0 | Fig 2.2.35 (a) | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||
Two-run technique | Butt weld test | 12 | 1 | Flat | 1.2~2.4 | Fig 2.2.35 (b) | Tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | |
19 | 1 | Flat | 4.0 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | ||||
NOTES: (1) Where approved by the Society, the diameter of electrodes or wires may be changed. (2) Tests on both multi-run and two run technique are to be conducted for multi-run and two run welding re- spectively and the number, dimensions and thickness of test assemblies, along with the grades and number of test specimens selected from each test assembly are to be according to each of the welding processes. However, longitudinal tensile test of two run technique are not required. | ||||||||
![]()
184 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
Table 2.2.52 Grades of Steel for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumables | Grade of steel for test assembly(1) |
RD 308, RY 308, RW 308, RU 308 | RSTS 304 |
RD 308L, RY 308L, RW 308L, R U 308L | RSTS 304L |
RD 309, RY 309, RW 309, RU 309 | RSTS 309S |
RD 309L, RY 309L, RW 309L | |
RD 309M o, RY 309M o, RW 309M o, RU 309M o | |
RD 309M oL, RW 309M oL | |
RD 310, RY 310, RW 310, RU 310 | RSTS 310S |
RY 310S | |
RD 310M o | |
RD 316, RY 316, RW 316, RU 316 | RSTS 316 |
RD 316L, RY 316L, RW 316L, R U 316L | RSTS 316L |
RD 317, RY 317, RW 317, RU 317 | RSTS 317 |
RD 317L, RY 317L, RW 317L, R U 317L | RSTS 317, RSTS 317L |
RY 321 | RSTS 321 |
RD 347, RY 347, RW 347, RU 347 | RSTS 321, RSTS 347 |
NOTE: (1) Notwithstanding the requirements in this table, mild steel or higher strength steel may be used for deposited metal test assembly. In this case, test assemblies are to be appropriately buttered. | |
(6) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment.
(7) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as- certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
4. Deposited metal test
(1) Welding of deposited metal test assemblies
(a) Test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.33 are to be welded in the flat position according to
the welding procedure recommended by the manufacturer.
![]()
(b) After each
150 but
![]()
run, the test assembly is to be left in still air until it has cooled to less than not below 15 , the temperature being taken at the centre of the weld on the
surface of seam.
(2) Chemical composition
(a) Deposited metals of electrodes for manual arc welding and of welding consumables for flux cored wire semi-automatic welding and submerged arc welding are to have the chemical composition given in Tables 2.2.53, 2.2.55 and 2.2.56 respectively.
(b) TIG and MIG welding consumables are to have the chemical composition of ladle analysis value complied with the requirements as given in Table 2.2.54.
(3) Deposited metal tensile test
(a) One tensile test specimens to be R10 shown in Table 2.2.1 is to be taken from each test
assembly. Further, where approved by the Society, one R14A
tensile test
specimen may be
taken, the longitudinal axis of test specimen coincides with mid- the centre thickness of plate.
of weld and the
(b)
(c)
![]()
The tensile test specimens may be subjected to a temperature not exceeding 250 for a pe- riod not exceeding 16 hours for hydrogen removal prior to testing.
Deposited metal tensile tests are to comply with the requirements in Table 2.2.57.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 185
![]()
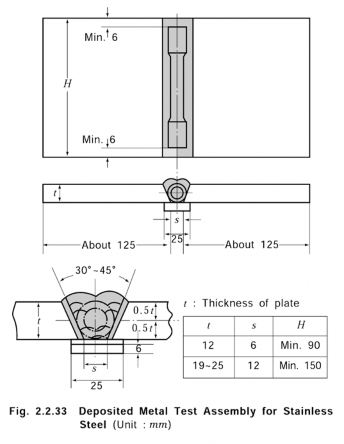
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.53 Chemical Composition of Deposited Metal for Electrodes
Grade | Chemical composition (%) | ||||||||
C(max.) | Si(max.) | Mn(max.) | P(max.) | S(max.) | Ni | Cr | Mo | Others | |
RD 308 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RD 308L | 0.04 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 12.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RD 309 | 0.15 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RD 309L | 0.04 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 16.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RD 309M o | 0.12 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RD 309M oL | 0.04 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RD 310 | 0.20 | 0.75 | 2.50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.0 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 |
| |
RD 310M o | 0.12 | 0.75 | 2.50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.0 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RD 316 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 2.75 | |
RD 316L | 0.04 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 16.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 2.75 | |
RD 317 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RD 317L | 0.04 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 16.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RD 347 | 0.08 | 0.90 | 2.50 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 |
| Nb8×C (%)~1.0 |
![]()
186 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()

Table 2.2.54 Chemical Composition of Deposited Metal for TIG Electrodes or MIG Wires
Grade
Chemical composition (%)
C(max.) | Si(max.) | Mn | P(max.) | S(max.) | Ni | Cr | Mo | Others | |
R Y 308 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 19.0 ~ 22.0 | ||
R Y 308L | 0.03 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 19.0 ~ 22.0 | ||
R Y 309 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 23.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
R Y 309L | 0.03 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 23.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RY 309M o | 0.12 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 23.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
R Y 310 | 0.15 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.5 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 | ||
R Y 310S | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.5 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 | ||
R Y 316 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
R Y 316L | 0.03 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
R Y 317 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 13.0 ~ 15.0 | 18.5 ~ 20.5 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
R Y 317L | 0.03 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 13.0 ~ 15.0 | 18.5 ~ 20.5 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
R Y 321 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 10.5 | 18.5 ~ 20.5 | Ti9×C (%) ~ 1.0 | |
R Y 347 | 0.08 | 0.65 | 1.0 ~ 2.5 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 19.0 ~ 21.5 | Nb10×C (%) ~ 1.0 | |
Table 2.2.55 Chemical Composition of Deposited Metal for Flux Cored Wire Semi-automatic Welding
![]()
![]()
(a) With Gas
Grade | Chemical composition (%) | ||||||||
C(max.) | Si(max.) | Mn | P(max.) | S(max.) | Ni | Cr | Mo | Others | |
RW 308 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RW 308L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 12.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RW 309 | 0.10 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RW 309L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RW 309M o | 0.12 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RW 309M oL | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RW 310 | 0.20 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.0 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 |
| |
RW 316 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RW 316L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RW 317 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RW 317L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 16.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RW 347 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 |
| Nb8×C (%) ~ 1.0 |
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 187
![]()
Table 2.2.55 Chemical Composition of Deposited Metal for Flux Cored Wire Semi-automatic Welding
(b) Without Gas
Grade | Chemical composition (%) | ||||||||
C(max.) | Si(max.) | Mn | P(max.) | S(max.) | Ni | Cr | Mo | Others | |
RW 308 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 19.5 ~ 22.0 |
|
|
RW 308L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 12.0 | 19.5 ~ 22.0 |
|
|
RW 309 | 0.10 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 23.0 ~ 25.5 |
|
|
RW 309L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 23.0 ~ 25.5 |
|
|
RW 309M o | 0.12 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
|
RW 309M oL | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
|
RW 310 | 0.20 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.0 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 |
|
|
RW 316 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 20.5 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
|
RW 316L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 20.5 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 |
|
RW 317 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 13.0 ~ 15.0 | 18.5 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 |
|
RW 317L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 13.0 ~ 15.0 | 18.5 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 |
|
RW 347 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 0.5 ~ 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 19.0 ~ 21.5 |
| Nb8×C (%) ~ 1.0 |
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.56 Chemical Composition of Deposited Metal for Submerged Arc Welding
Grade | Chemical composition (%) | ||||||||
C(max.) | Si(max.) | Mn(max.) | P(max.) | S(max.) | Ni | Cr | Mo | Others | |
RU 308 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RU 308L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 12.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | ||
RU 309 | 0.15 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | ||
RU 309M o | 0.12 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 22.0 ~ 25.0 | 2.0 ~ 3.0 | |
RU 310 | 0.20 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 20.0 ~ 22.0 | 25.0 ~ 28.0 |
| |
RU 316 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 14.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 2.75 | |
RU 316L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 11.0 ~ 16.0 | 17.0 ~ 20.0 | 2.0 ~ 2.75 | |
RU 317 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 14.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RU 317L | 0.04 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 12.0 ~ 16.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 | 3.0 ~ 4.0 | |
RU 347 | 0.08 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 9.0 ~ 11.0 | 18.0 ~ 21.0 |
| Nb8×C (%) ~ 1.0 |
![]()
188 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.57 Tensile Test Requirements for Deposited Metal
Electrode for manual arc welding | Consumables for TIG and MIG welding | Flux cored wire for semi-automatic welding | Consumables for submerged arc welding | Tensile strength ( ) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation (%) |
RD 308 | RY 308 | RW 308 | RU 308 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 35 min. |
RD 308L | RY 308L | RW 308L | RU 308L | 510 min. | 205 min. | 35 min. |
RD 309 | RY 309 | RW 309 | RU 309 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
RD 309L | RY 309L | RW 309L | 510 min. | 205 min. | 30 min. | |
RD 309M o | RY 309M o | RW 309M o | RU 309M o | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
RD 309M oL | RW 309M oL | 510 min. | 205 min. | 30 min.(1) | ||
RD 310 | RY 310 | RW 310 | RU 310 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
RY 310S | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. | |||
RD 310M o | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. | |||
RD 316 | RY 316 | RW 316 | RU 316 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
RD 316L | RY 316L | RW 316L | RU 316L | 510 min. | 205 min. | 35 min. |
RD 317 | RY 317 | RW 317 | RU 317 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
RD 317L | RY 317L | RW 317L | RU 317L | 510 min. | 205 min. | 30 min. |
RY 321 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. | |||
RD 347 | RY 347 | RW 347 | RU 347 | 550 min. | 225 min. | 30 min. |
NOTE: (1) Elongation of R W 309M oL is to be not less than 20 (%). | ||||||
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
5. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies
(a) Test assemblies as shown in Figs 2.2.34 and 2.2.35 are to be welded in each welding po- sition (flat, horizontal, vertical upward, vertical downward and overhead) which is recom-
![]()
![]()
mended by the manufacturer.
(b)
A15f0ter eabcuht runnot, tbhelotewst 1a5ssem, btlhye istetmo pbeeratluerfet
surface of seam.
bineinsgtiltlakaeinr
autnttihl e itcehnatrse coofoltehde wtoeldlesosn ththaen
(2) Butt weld tensile test
(a) One tensile test specimens to be R2A shown in Table 2.2.1 is to be taken from each test assembly.
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
The tensile strength of each test specimen is to comply with the requirements given in
Table 2.2.58.
![]()
Submerged arc welding materials used only in the two-run technique are to be selected as one R14A tensile test specimen of Table 2.2.1, such that the longitudinal centre line of the test specimen coincides with the weld centre line of the test assemblies and centre of thickness.
Tthhee hloenatgitturedaitnmalentetnsniolet teexsct eesdpiencgim2e5n0s spefocirfiead peinriotdhenoptreecxecdeiendgin(g3)16mahyourbse fosur bhjeycdtreodgetno
removal prior to testing.
The tensile strength, yield point and elongation of the test specimens specified in the pre-
ceding (c) and (d) are to comply with the requirements given in Table 2.2.57.
(3) Butt weld bend test
(a) The face and root bend test specimens are to be RB4 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2, and test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly.
(b)
The test specimens are to be capable of withstanding, without crack exceeding 3 mm long
on the outer surface of the specimen or other defects,
degrees over a former having a radius of 1.5 times the
being bent through an angle of 120
thickness of test specimen.
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 189
![]()
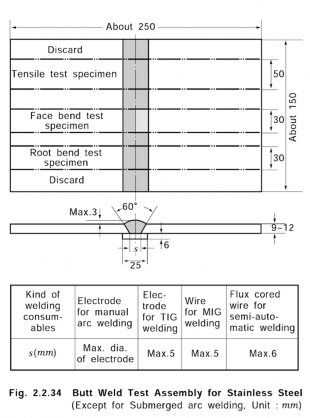
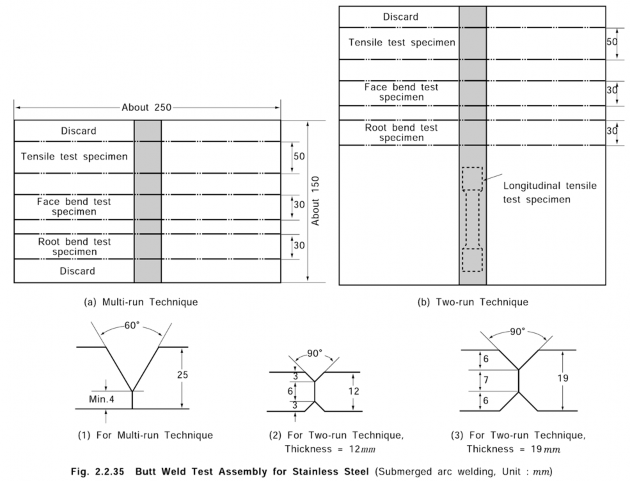
![]()
190 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.58 Tensile Test Requirements for Butt Weld
Electrode for manual arc welding | Consumables for TIG and MIG welding | Flux cored wire for semi-automatic welding | Consumables for submerged arc welding | Tensile strength ( ) |
RD 308 | RY 308 | RW 308 | RU 308 | 520 min. |
RD 308L | RY 308L | RW 308L | RU 308L | 480 min. |
RD 309 | RY 309 | RW 309 | RU 309 | 520 min. |
RD 309L | RY 309L | RW 309L | 520 min. | |
RD 309M o | RY 309M o | RW 309M o | RU 309M o | 520 min. |
RD 309M oL | RW 309M oL | 520 min. | ||
RD 310 | RY 310 | RW 310 | RU 310 | 520 min. |
RY 310S | 520 min. | |||
RD 310M o | 520 min. | |||
RD 316 | RY 316 | RW 316 | RU 316 | 520 min. |
RD 316L | RY 316L | RW 316L | RU 316L | 480 min. |
RD 317 | RY 317 | RW 317 | RU 317 | 520 min.(1) |
RD 317L | RY 317L | RW 317L | RU 317L | 520 min.(1) |
RY 321 | 520 min. | |||
RD 347 | RY 347 | RW 347 | RU 347 | 520 min. |
NOTE: (1) Where the test assembly is made of R STS 317L, the tensile strength is not to be less than 480 . | ||||
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
6. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspections, tests specified in the following (2) are to be conducted for each brand of approved consumables, and they are to be passed satisfactorily.
(2) The kinds of test, etc. in the annual inspections are to be as given in Table 2.2.59.
(3) The welding procedures and requirements of be as specified in Pars 4 through 5.
test assemblies for tests in the preceding (2) are to
Table 2.2.59 Kinds of Test at Annual Inspection
Kind of welding consumables | Kind of test | Welding procedure for test assembly | Kind and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||||
Welding position | Dia. of electrode or wire (mm) | Number | Dimension | Thickness (mm) | ||||
Electrode for manual arc welding | Deposited metal test | Flat | 3.2 ~ 4.0 | 1 | Fig 2.2.33 | 12 ~ 19 | Tensile test specimen: 1 | |
Consumables for TIG welding | 2.4 ~ 3.2 | |||||||
Consumables for MIG welding | 1.2 ~ 1.6 | |||||||
Flux cored wire for semi-automatic welding | 1.2 ~ 3.2 | |||||||
Consumables for submerged arc welding (1) | Multi-run technique | Deposited metal test | Flat | 1.2 ~ 4.0 | 1 | Fig 2.2.33 | 19 ~ 25 | Tensile test specimen: 1 |
Two-run technique | Butt weld test | Flat | 2.4 ~ 4.0 | 1 | Fig 2.2.35(b) | 12 ~ 19 | Tensile test specimen: 1 Longitudinal tensile test specimen: 1 Face bend specimen: 1 Root bend specimen: 1 | |
NOTE: (1) Tests on both multi-run and two run technique are to be conducted for multi-run and two run welding respectively and the number, dimensions and thickness of test assemblies, along with the grades and num- ber of test specimens selected from each test assembly are to be according to each of the welding processes. However, longitudinal tensile test of two run technique are not required. | ||||||||
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 191
![]()
608. Welding consumables for aluminium alloys
1. Application
(1) Welding consumables (b)(hereinafter referred and annual inspections
used for aluminium alloys mentioned in the following (a) and to as "welding consumables") are to be subjected to the approval tests in accordance with these requirements.
(a) Rod-gas combinations for tungsten inert gas arc welding (TIG welding) or plasma arc weld- ing
(b) Wire electrode and wire-gas combinations for metal arc inert gas welding (MIG welding), tungsten inert gas arc welding(TIG welding) or plasma arc welding
(2) Where no special requirements are given herein, e.g. for the approval procedure or for the
welding of test assemblies and testing, those as specified in 601. through 605. apply in analo- gous manner.
2. Grades and marks of welding consumables
(1) Grades and marks of welding consumables are classified as given in Table 2.2.60.
Table 2.2.60 Grades and Marks
Kind of welding consumables | Grade and Mark |
Electrode | RA, RB, RC, RD |
Wire | W A, W B, W C, W D |
(2) Approval of a wire or a rod will be granted in conjunction with a specific shielding gas ac- cording to Table 2.2.58 with suffixed mark “G”(e.g. R B G (I-3)). or defined in terms of composi- tion and purity of “special” gas to be designated with group sign “S”(eg. R B S( CO 2 100%). The
composition of the shielding gas is to be reported. The approval of a wire or rod with any par-
ticular gas can be applied or transferred to any combination of the same wire or rod and any gas in the same numbered group as defined in Table 2.2.61, subject to the agreement of the Society.
Table 2.2.61 Kind of Gas
Group | Kinds | Gas composition(%) | |
He | Ar | ||
I | I-1 | - | 100 |
I-2 | 100 | - | |
I-3 | > 0 - 33 | Rest | |
I-4 | > 33 - 66 | Rest | |
I-5 | > 66 - 95 | Rest | |
S | Others | ||
3. General provisions of tests
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness and dimensions of specimen taken from each test assembly for welding 2.2.62.
(2) The aluminium alloys used in preparation for test sumables are to be as given in Table 2.2.63.
test assemblies, kind and number of test consumables are to be as given in Table
assembly corresponding to welding con-
(3) For the approval of welding consumables, the tests specified in (1) are to be successfully con- ducted for each brand of welding consumables.
(4) For welding consumables using
a shielding gas, the tests specified in (1) are to be conducted
for each kind of gas designated among Table 2.2.61 by the manufacturer. However, where the
manufacturer designates several
kinds of gas which are classified into the group l in Table
2.2.61 and the tests specified in (1) are to be conducted for any one kind of gas, the tests for the other kind of gas may be dispensed with subject to the approval of the Society.
![]()
192 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.62 Kinds of Test for Welding Consumables
Kinds of test | Test assembly | Kinds and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||
Welding position | Number | Dimension | Thickness (mm) | ||
Deposited metal test (Chemical composition test) | Flat | 1 | Fig 2.2.36 | - | - |
Butt weld test | Flat | 1 | Fig 2.2.37 | 10 12 | Tensile test specimen : 2 Face bend test specimen : 2 Root bend test specimen : 2 Macro structure test specimen : 1 |
Horizontal | 1(1) | ||||
Vertical upward | 1 | ||||
Overhead | 1 | ||||
Flat | 1 | Fig 2.2.38 | 20 ~ 25 | Tensile test specimen : 2 Face bend test specimen : 2 Root bend test specimen : 2 Macro structure test specimen : 1 | |
Note (1) Welding consumables satisfying the requirements for flat and vertical upward positions may be dispensed with the tests for horizontal position subject to the approval of the Society. | |||||
Table 2.2.63 Grade of Aluminium Alloys used for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumables | Grade of aluminium alloys used for test assembly | |
R A , W A | 5000 series | 5754 |
R B , W B | 5086 | |
R C , W C | 5083, 5383, 5456, 5059 | |
R D , W D | 6000 series | 6005A, 6061, 6082 |
Note: Approval on higher strength AlM g base materials(5000 series) covers also the lower strength A lM g grades and their combination with A lSi grades | ||
(5) When the manufacturer designated the gas classified into the group "S" in the tests specified in (4), the composition of the shielding gas is to be reported to the Society.
(6) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any heat treatment or peening.
(7) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a radiographic examination to as- certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
4. Deposited metal test
(1) Welding of deposited metal test assembly
(a) The test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.36 are to be welded in flat position in accordance with the welding process designated by the manufacturer.
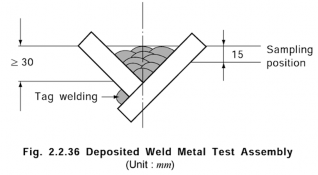
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 193
![]()
(b) The size of test assembly corresponding to the welding consumables and welding process is to be taken a sufficient amount of pure weld metal for chemical analysis.
(2) Chemical composition The chemical composition of the welding consumables is to be de- termined by the analysis of the deposited weld metal specified in Fig 2.2.36 and the results of the analysis are to comply with the limit value specified by the manufacturer.
5. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assemblies
(a) The test assemblies as shown in Fig 2.2.37 are to be welded in each welding position des-
ignated by the manufacturer (downhand, horizontal, vertical-upward and overhead). The test assembly as shown by Fig 2.2.38 is to be welded in the downhand position.
(b)
On completion of each run, the test assemblies are to be allowed to cool naturally in air until the temperature measured at the surface of the centre of the welding joint is ambient temperature. However, the test assemblies for R D and W D are to be allowed to naturally
ageing for a minimum period of 72 hours from the completion of welding before testing.
(2) Butt weld tensile test
(a) The tensile test specimens are to be R 2A specimen shown in Table 2.2.1 and two test specimens are to be taken from each test assembly.
(b)
The tensile strength is to comply with the requirements as given in Table 2.2.64.
![]()
Table 2.2.64 Requirements for the transverse tensile and bend tests
Grade of welding consumables | Base material used for the test | Tensile strength ( ) | Bend test | |
Former diameter (mm) | Bending angle | |||
R A /W A | 5754 | 190 min. | 3 t(1) | 180° |
R B /W B | 5086 | 240 min. | 6 t(1) | |
R C /W C | 5083 | 275 min. | ||
5383, 5456 | 290 min. | |||
5059 | 330 min. | |||
R D /W D | 6061, 6005A, 6082 | 170 min. | ||
Note (1) t : Thickness of the test specimen | ||||
(3) Butt Weld Bend Test
(a) The face bend and root bend test specimens are to be R B 4 specimen shown in Table 2.2.2 and two test specimens are to be taken from each assembly.
(b)
The test specimens are to sustain the face and root bend tests over 180" using a former having a diameter in accordance with Table 2.2.64, without cracks exceeding 3 m m in
length and other any defects on the outer surface.
(4) Butt weld macro structure test
(a) One macro structure test specimen as shown in Fig 2.2.37 and Fig 2.2.38 is to be taken from the butt weld test assembly.
(b) The macro structure test specimen is to be examined that there are not any imperfections such as lack of fusion, poor penetration or cracks.
6. Annual inspections
(1) In the annual inspections, every approved welding consumables are to be subjected to the tests provided in (2) and are to be successfully examined.
(2) Kinds of tests in the annual inspections are to be as given in Table 2.2.65.
(3) The welding procedure and requirements for test assemblies specified in (2) are to be in ac- cordance with the requirements in 4. to 5.
![]()
194 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
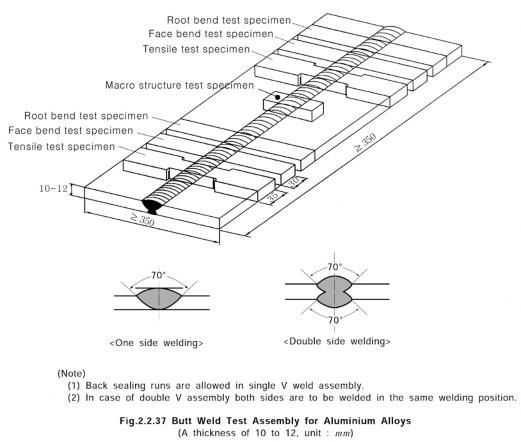
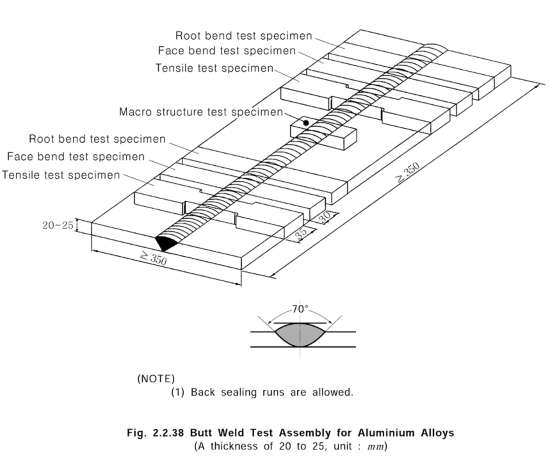
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 195
![]()
Table 2.2.65 Kinds of Tests in Annual Inspections
Kinds of test | Test assembly | Kind and number of test specimens taken from test assembly | |||
Welding position | Number | Dimensions | Thickness (mm) | ||
Deposited weld metal test(Chemical composition Analysis) | Flat | 1 | Fig 2.2.36 | - | - |
Butt weld test | Flat | 1 | Fig 2.2.37 | 10 - 12 | Tensile test specimen : 2 Face bend test specimen : 2 Root bend test specimen : 2 Macro structure test specimen : 1 |
609. Welding consumables for high strength quenched and tempered steels
1. Application
Welding consumables for high strength quenched and tempered steels, which are given in following
(1) through (3) (hereinafter referred to as "welding consumables" in 609.) the approval test and an- nual inspections are to be in accordance with the requirements specified in 609.
(1) Electrodes for manual arc welding(specified in 602. 1 (1) and (2))
(2) Automatic welding consumables(specified in 603. 1 (1) and (2). However, in this case, used on- ly for multi-run technique in principle.)
(3) Semi-automatic welding consumables
2. Grade and marks of welding consumables
(1) Grades and marks of welding consumables are classified as given in Table 2.2.67.
(2) Where the welding consumables have passed the test specified in 3 (1) below, the suffixes are to be added to the grade marks with the same methods as specified in 603. 2 (2) and (3) or 604. 2 (2) and (3) according to the grade of welding consumables.
(3) For low hydrogen electrodes which have passed the hydrogen test specified in 6. the suffixes given in Table 2.2.70 are to be added to the grade marks (eg. 3Y 46S H 5).
3. General provisions for tests
(1) Kinds of test, number, thickness, and dimensions of test assembles, diameters of electrodes or wires used for welding and welding positions, together with kinds and number of test specimens taken from each test assembly for welding consumables are to be in accordance with the re- quirements specified in 602. 3., 603. 3. or 604. 3. However, note (4) of Table 2.2.17 and note (5) of Table 2.2.34 are not to be required. Provisions for automatic welding consumables are to be the requirements specified in multi run technique.
(2) The grades of steels used for tests are to be those given in Table 2.2.66 corresponding to the grades of welding consumables, or those which are considered equivalent by the Society.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.66 Grade of Steels for Test Assembly
Grade of welding consumables | Grade of steel for assembly |
2Y 42, 2Y 46, 2Y 50, 2Y 55, 2Y 62, 2Y 69 | A H 43 A H 70 |
3Y 42, 3Y 46, 3Y 50, 3Y 55, 3Y 62, 3Y 69 | A H 43 A H 70, D H 43 D H 70 |
4Y 42, 4Y 46, 4Y 50, 4Y 55, 4Y 62, 4Y 69 | A H 43 A H 70, D H 43 D H 70, E H 43 E H 70 |
5Y 42, 5Y 46, 5Y 50, 5Y 55, 5Y 62, 5Y 69 | A H 43 A H 70, D H 43 D H 70, E H 43 E H 70, F H 43 F H 70 |
NOTES: Notwithstanding the requirements in this table, normal and higher strength steels may be used for de- posited metal test assembly. In this case, appropriate buttering is to be carried out. | |
![]()
196 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
(3) For the approval of welding consumables, the tests specified in conducted for each brand of welding consumables.
(4) After welding, the test assemblies are not to be subjected to any
(5) It is recommended that the welded assemblies be subjected to a
602., 603. or 604. are to be
heat treatment or peening. radiographic examination to as-
certain that there are any defects in the weld prior to the preparation of test specimens.
4. Deposited metal test
(1) Welding of deposited metal test assembly
Welding sequence of test assemblies are to be in accordance with the requirements specified in
602. 4 (1), 603. 4 (1) or 604. 4 (1) appropriate to the grade of the welding consumables.
(2) Chemical composition
(a) The chemical composition of the deposited weld metal shall be determined by the manu- facturer and reported the results of the analysis to the Society. The report is also to include the main alloy elements.
(b) The results of the analysis shall not exceed the limit values specified in the standards or by the manufacturer, the narrower tolerances being applicable in each case.
(3) Deposited metal tensile test
(a) Kinds, numbers and selection methods of the deposited metal tensile test specimens being taken from each test assembly are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 4 (3), 603. 4 (3) or 604. 4 (3) according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(b) The tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of each test the requirements specified in Table 2.2.67 according to consumables.
specimen are to comply with the grade of the welding
(c)
The provisions specified in the preceding 602. 4 (3) (b) may specimens.
be applied to the tensile test
(4) Deposited metal impact test
(a) Kinds, numbers and selection methods of the deposited metal impact test specimens being taken from each test assembly are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 4 (4), 603. 4 (4) or 604. 4 (4) according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(b)
The test temperature and minimum mean absorbed energy are to comply with the require- ments specified given in Table 2.2.67 according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(c) The requirements specified in the preceding 602. 4 (4), (b) and (d) are to be applied to this test.
5. Butt weld test
(1) Welding of butt weld test assembly
Welding sequence of test assemblies are to be in accordance with the requirements specified in
602. 5 (1), 603. 5 (1) or 604. 5 (1) appropriate to the grade of the welding consumables.
(2) Butt weld tensile test
(a) Kinds and numbers of the butt weld tensile test specimens being taken from each test as- sembly are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 5 (2), 603. 5 (2) or 604. 5
(2) according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(b) The tensile strength of each test specimen is to meet the requirements given in Table
2.2.68 according to the grade of the welding consumables.
![]()
Table 2.2.68 Tensile Test Requirements for butt weld test
Grade of welding consumables | Tensile strength ( ) |
2Y 42, 3Y 42, 4Y 42, 5Y 42 | 530 min. |
2Y 46, 3Y 46, 4Y 46, 5Y 46 | 570 min. |
2Y 50, 3Y 50, 4Y 50, 5Y 50 | 610 min. |
2Y 55, 3Y 55, 4Y 55, 5Y 55 | 670 min. |
2Y 62, 3Y 62, 4Y 62, 5Y 62 | 720 min. |
2Y 69, 3Y 69, 4Y 69, 5Y 69 | 770 min. |
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 197
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.67 Test Requirements for Deposited Metal
Grade of welding consumables | Tensile test | Impact test | |||
Tensile strength ( )(1) | Yield strength ( ) | Elongation (%) | Test temp ( ) | Minimum mean absorbed energy(J) | |
2Y 42 | 530 680 | 420 min. | 20 min. | 0 | 47 min. |
3Y 42 | -20 | ||||
4Y 42 | -40 | ||||
5Y 42 | -60 | ||||
2Y 46 | 570 720 | 460 min. | 20 min. | 0 | |
3Y 46 | -20 | ||||
4Y 46 | -40 | ||||
5Y 46 | -60 | ||||
2Y 50 | 610 770 | 500 min. | 18 min. | 0 | 50 min. |
3Y 50 | -20 | ||||
4Y 50 | -40 | ||||
5Y 50 | -60 | ||||
2Y 55 | 670 830 | 550 min. | 18 min. | 0 | 55 min. |
3Y 55 | -20 | ||||
4Y 55 | -40 | ||||
5Y 55 | -60 | ||||
2Y 62 | 720 890 | 620 min. | 18 min. | 0 | 62 min. |
3Y 62 | -20 | ||||
4Y 62 | -40 | ||||
5Y 62 | -60 | ||||
2Y 69 | 770 940 | 690 min. | 17 min. | 0 | 69 min. |
3Y 69 | -20 | ||||
4Y 69 | -40 | ||||
5Y 69 | -60 | ||||
Note Tensile strength specified in the table may be alerted where deemed appropriate by the Society. | |||||
![]()
![]()
![]()
(3) Butt weld bend test
(a) Kinds and numbers of the butt weld face bend and root bend test specimens being taken
hom each test assembly are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 5 (3) or 604. 5 (3) according to the grade of the welding consumables.
5 (3), 603.
(b) The test specimens are to be subjected to face bend and root bend tests by using former
having a radius given in Table 2.2.69. Outer surface of the specimens is to be free from
any cracks exceeding 3 mm long or other defects when they are degrees.
bent to the angle of 120
Table 2.2.69 Bend Radius for Butt Weld Bend Test
Grade of welding consumable | Radius of plunger | |||||||
2Y 42 | 50, | 3Y 42 | 50, | 4Y 42 | 50, | 5Y 42 | 50 | 2.0 |
2Y 55 | 69, | 3Y 55 | 69, | 4Y 55 | 69, | 5Y 55 | 69 | 2.5 |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(c) Where the bending angle 120° is not achieved, the specimen may the requirements, if the bending elongation on a gauge length Lo
be considered as fulfilling shown in Fig 2.2.39 ful-
fills the minimum elongation requirements stated in Table 2.2.67 of the Rules
![]()
198 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
![]()
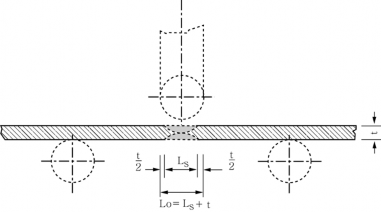
Fig 2.2.39 gauge length Lo
(4) Butt weld impact test
(a) Kinds, numbers and selection method of the butt weld impact test specimens being taken
from each test assembly are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 5 (4), 603. 5 (4) or 604. 5 (4) according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(b)
Testing temperature and minimum mean absorbed energy are to comply with the require- ments specified in Table 2.2.67 according to the grade of the welding consumables.
(c) The requirements specified in the preceding 602. 5 (4), (b) and (d) are to be applied to these tests.
6. Hydrogen test
(1) Hydrogen Test is to be carried out for welding consumables except gas shielded arc solid wire by the glycerine method, mercury method, gas chromatographic method or other methods deemed appropriate by the Society.
(2) The average volume of hydrogen is to comply with the requirements specified in Table 2.2.70 according to the test procedures specified in preceding (1) or the type of suffixes to be added to the grade marks.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Table 2.2.70 Requirements for hydrogen Contents
Grade of welding consumable | Suffixes | Requirements for Hydrogen Contents ( ) | ||
Glycerine method | Mercury method | Gas chromatographic method | ||
2Y 42 50, 3Y 42 50, 4Y 42 50, 5Y 42 50 | H 10 | 0.05 max. | 0.10 max. | 0.10 max. |
2Y 55 69, 3Y 55 69, 4Y 55 69, 5Y 55 69 | H 5 | - | 0.05 max. | 0.05 max. |
7. Fillet weld test assemblies
(1) Welding of fillet weld test assemblies The test assemblies are to be in accordance with the re- quirements in 602. 7 (1).
(2) Fillet weld macro-structure test The macro-structure test is to be correspondingly in accord-
ance with the requirements in 602. 7 (2).
(3) Fillet weld hardness test The hardness test is to be correspondingly in accordance with the re- quirements in 602. 7 (3).
(4) Fillet weld fracture test The fracture test is to be correspondingly in accordance with the re- quirements in 602. 7 (4).
![]()
Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015 199
![]()
8. Annual inspections
Annual inspections are to comply with the requirements specified in 602. 8, 603. 8 or 604. 8 ac- cording to the grade of the welding consumables. However, in general, annual inspections for auto- matic welding consumables are to comply with the requirements specified for multi run technique.
9. Change in grades
The changes in grades relating to the strength or toughness of approved welding consumables are
to comply with the requirements the welding consumables. ![]()
specified in
602. 9, 603.
9 or
604.
9 according to the grade of
![]()
200 Rules for the Classification of Steel Ships 2015
